A new study, drawing upon a synthesis of genetic, paleoecological, and archaeological evidence, has pinpointed the Persian Plateau (Iranian Plateau) as a pivotal geographical hub for Homo sapiens during the initial stages of their migration out of Africa. This research challenges previous ᴀssumptions regarding the dispersal of human populations into Eurasia.
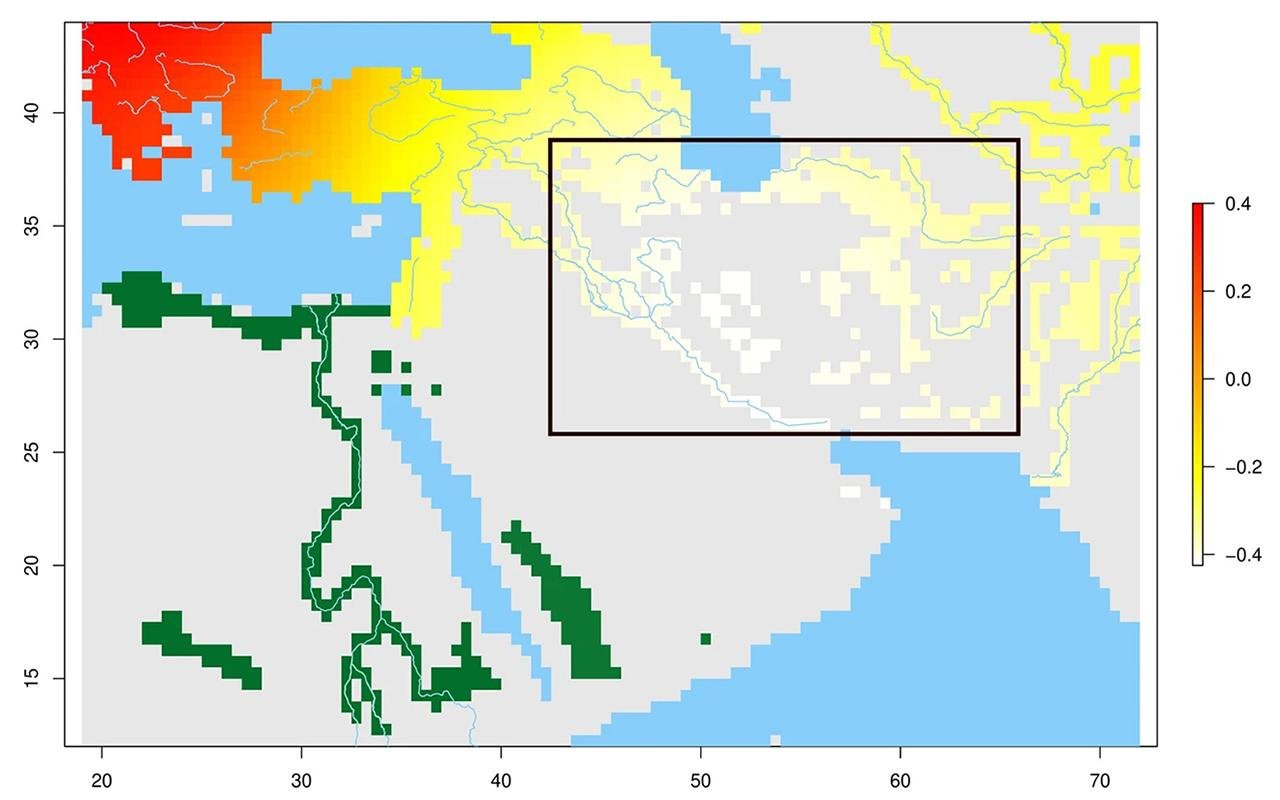 Combination of palaeoecological and genetic analyses. In light yellow, within the black frame, are geographic locations that are putative Hub focal areas and predicted habitable areas. In green are the habitable areas that might have hosted the Basal Eurasian population. Credit: Vallini, L et al., Nature Communications 2024
Combination of palaeoecological and genetic analyses. In light yellow, within the black frame, are geographic locations that are putative Hub focal areas and predicted habitable areas. In green are the habitable areas that might have hosted the Basal Eurasian population. Credit: Vallini, L et al., Nature Communications 2024
Published in Nature Communications, the study provides a comprehensive understanding of human migration patterns between approximately 70,000 to 45,000 years ago. During this critical period, Homo sapiens did not uniformly spread across Eurasia, leaving a gap in our comprehension of their whereabouts.
Key findings from the research include the identification of the Persian Plateau as a primary region for early human settlement. Through genetic analysis and paleoecological modeling, researchers revealed that waves of human populations originating from the Persian Plateau ultimately populated all of Eurasia. This region emerged as a favorable habitat capable of supporting larger populations compared to surrounding areas in West Asia.
The study’s genetic component underscores the long-lasting differentiation of populations in the Persian Plateau, indicating its significance as a pivotal location for early human settlement and subsequent migrations. By disentangling 40,000 years of admixture and other confounding events, researchers identified a genetic connection that emphasizes the Plateau’s role in shaping human history.
 Researchers working on Pebdeh Cave in the southern Zagros Mountains. Pebdeh was occupied by hunter-gatherers as early as 42,000 years ago. Credit: Mohammad Javad Shoaee / Griffith University
Researchers working on Pebdeh Cave in the southern Zagros Mountains. Pebdeh was occupied by hunter-gatherers as early as 42,000 years ago. Credit: Mohammad Javad Shoaee / Griffith University
Professor Michael Petraglia, Director of Griffith University’s Australian Research Center for Human Evolution and co-author of the study, said: “Our multidisciplinary study provides a clearer view of the ancient past, offering insights into the critical period between the Out of Africa expansion and the differentiation of Eurasian populations. The Persian Plateau emerges as a key region, underlining the need for further archaeological explorations.”
Leonardo Vallini of the University of Padova, Italy, first author of the study, highlighted the broader implications of the discovery: “The revelation elucidates a 20,000-year portion of Homo sapiens’ history outside of Africa, shedding light on interactions with Neanderthal populations and providing crucial clues for understanding the demographic history of our species across Europe, East Asia, and Oceania.”
Senior author Professor Luca Pagani added, “The discovery of the Persian Plateau as a hub for early human migration opens new avenues for archaeological exploration, enriching our understanding of our species’ journey across continents and highlighting this region’s pivotal role in shaping human history.”
The study’s findings corroborate with previous debates on human migration patterns, providing the first comprehensive picture of the ancestors of present-day non-Africans during the early colonization of Eurasia. Pagani noted, “Our results provide the first full picture of the whereabouts of the ancestors of all present-day non-Africans in the early phases of the colonization of Eurasia.”
Petraglia added: “This study is a story about us and our history – our goal was to unravel some of the mystery about our evolution and our worldwide dispersal.” The study offers a comprehensive understanding of human migration patterns and highlights the significance of the Persian Plateau in shaping the course of human history.
Griffith UniversityMore information: Vallini, L., Zampieri, C., Shoaee, M.J. et al. (2024). The Persian plateau served as hub for Homo sapiens after the main out of Africa dispersal. Nat Commun 15, 1882. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-46161-7





