Ötzi the Iceman, a mummified individual discovered in the Ötztal Alps in 1991, has long captivated researchers with his enigmatic tattoos. The latest study, published in the European Journal of Archaeology, challenges previous ᴀssumptions about how these tattoos were created, suggesting they were made through a method known as hand-poking.
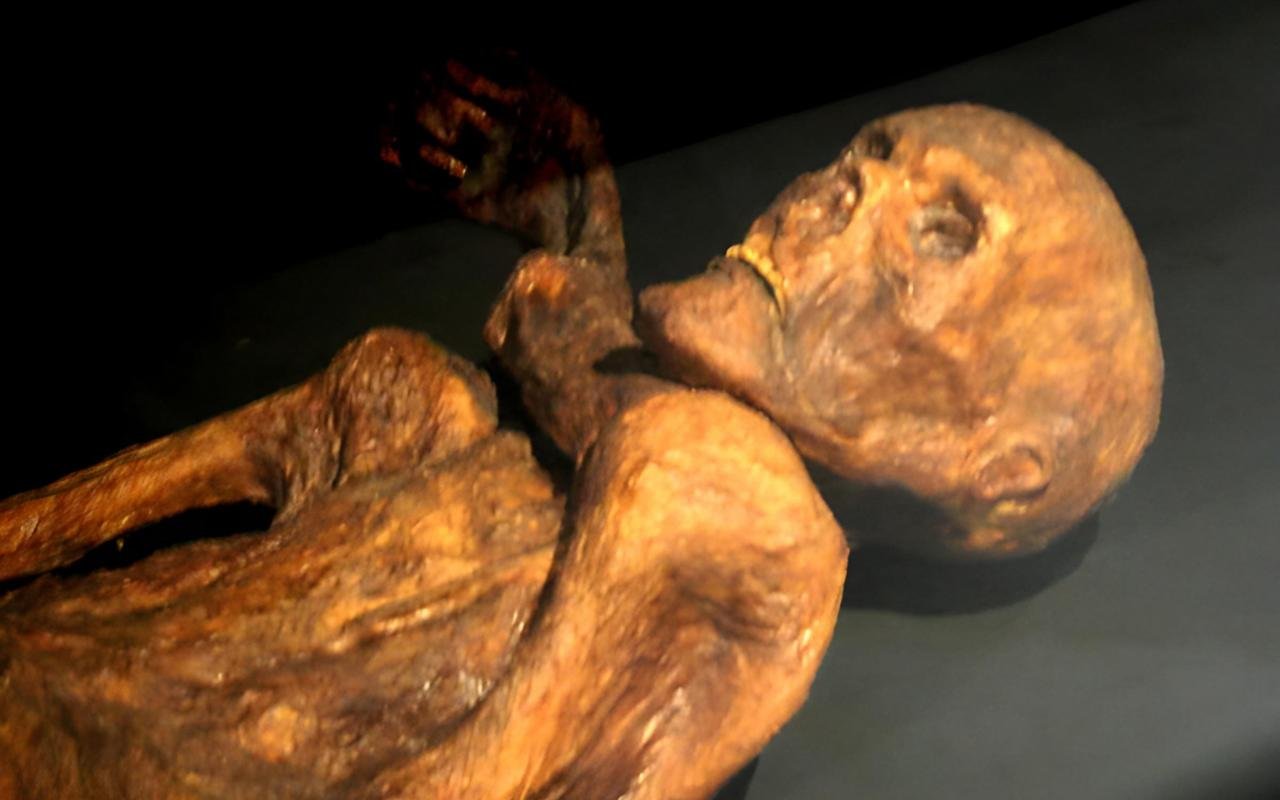 Ötzi the ice mummy. Credit: Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0
Ötzi the ice mummy. Credit: Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0
The Iceman, who lived approximately 5,300 years ago, was found to have 61 tattoos adorning various parts of his body, including his lower back, abdomen, left wrist, and lower legs. These tattoos, consisting of black lines and crosses, have long been a subject of speculation among scientists and historians.
Researchers, including archaeologists, historians, and tattoo artists, collaborated to investigate Ötzi’s tattoos. Contrary to prior theories proposing incisions followed by soot application, this study suggests that Ötzi’s tattoos were likely created using hand-poking with a single-pointed tool, possibly made from bone or copper.
The team conducted an experiment involving tattooing on modern skin to replicate Ötzi’s tattoos using different ancient techniques: hand-poking, subdermal tattooing, hand tapping, and incision. Tattoo artist Danny Riday volunteered for the experiment, using various tools such as animal bones, copper, obsidian, and even a boar tusk to create the tattoos.
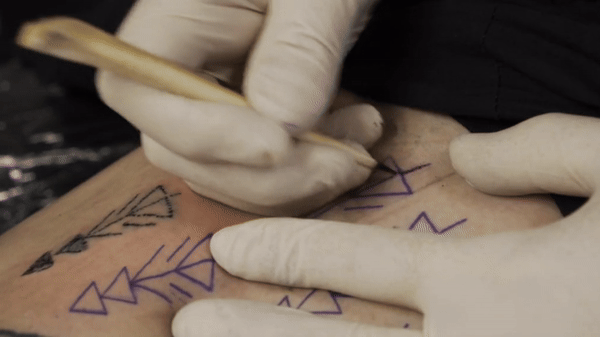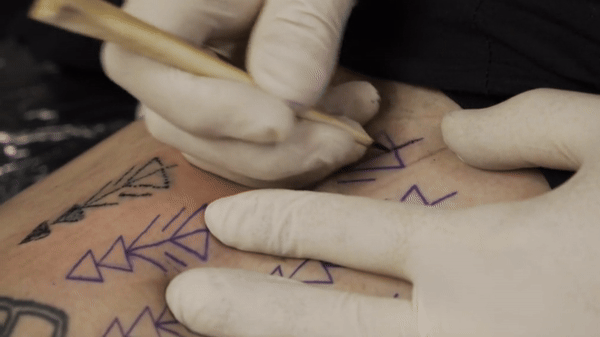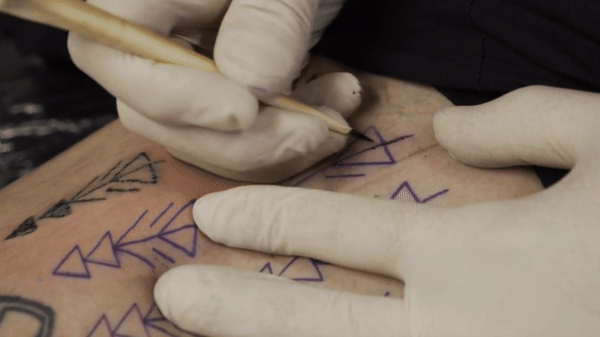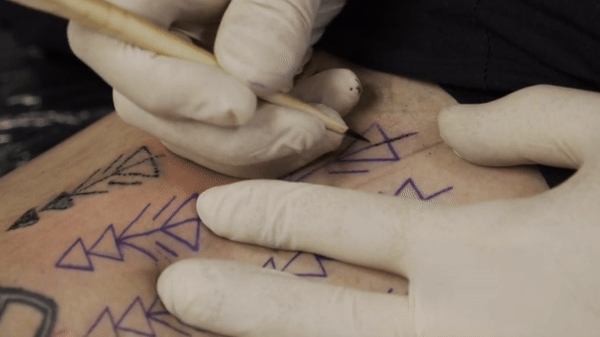 Co-author Danny Riday tattooing his own leg using an awl made from the bone of a white-tailed deer. Comparisons indicate that this was the technique used for all of Otzi’s 61 tattoos. Credit: Danny Riday
Co-author Danny Riday tattooing his own leg using an awl made from the bone of a white-tailed deer. Comparisons indicate that this was the technique used for all of Otzi’s 61 tattoos. Credit: Danny Riday
After allowing the tattoos to heal, the researchers compared them with Ötzi’s tattoos through detailed imagery. They found that the hand-poking method closely matched the characteristics of Ötzi’s tattoos, which consisted of short, straight lines resulting in tiny, overlapping disks forming a line pattern.
Archaeologist Aaron Deter-Wolf, lead author of the study and an expert in ancient tattoos, highlighted the significance of discernible variations in tattoos created using different tools and techniques, which can aid in the study of preserved remains from archaeological collections and shed light on ᴀssociated cultures.
The study also suggests that tattooing was a widespread skill in Ötzi’s time. Contrary to popular perceptions of ‘primitive’ humans, the research demonstrates that ancient peoples possessed advanced knowledge and techniques in various aspects of daily life, including body modification.
Furthermore, the study raises questions about the purpose of Ötzi’s tattoos. While some researchers have speculated that they were used for medicinal purposes or as a form of early acupuncture, the exact significance of the tattoos remains unclear. Further research is needed to unravel the mysteries surrounding Ötzi’s tattoos and their cultural significance.
More information: Deter-Wolf A, Robitaille B, Riday D, Burlot A, Sialuk Jacobsen M. (2024). Chalcolithic Tattooing: Historical and Experimental Evaluation of the Tyrolean Iceman’s Body Markings. European Journal of Archaeology:1-22. doi:10.1017/eaa.2024.5





