An international team of researchers, led by Peruvian bioarchaeologist Luis Pezo-Lanfranco, has shed new light on a tumultuous period in the Central Andes, specifically in the Supe Valley region of present-day Peru, during the transition from the fifth to the fourth century BCE. This period, marking the shift from the Middle Formative to the Late Formative period, was characterized by significant political upheaval and intergroup violence.
The study focused on skeletal remains unearthed from a burial site near the ancient ceremonial center of Caral. The team meticulously examined the remains of 67 individuals dating back to 500-400 BCE and discovered a staggering 80% of adults and adolescents bore injuries indicative of violent encounters. Perimortem injuries, observed in the skull, face, and thorax, suggested lethal interpersonal violence, with victims including men, women, and children.
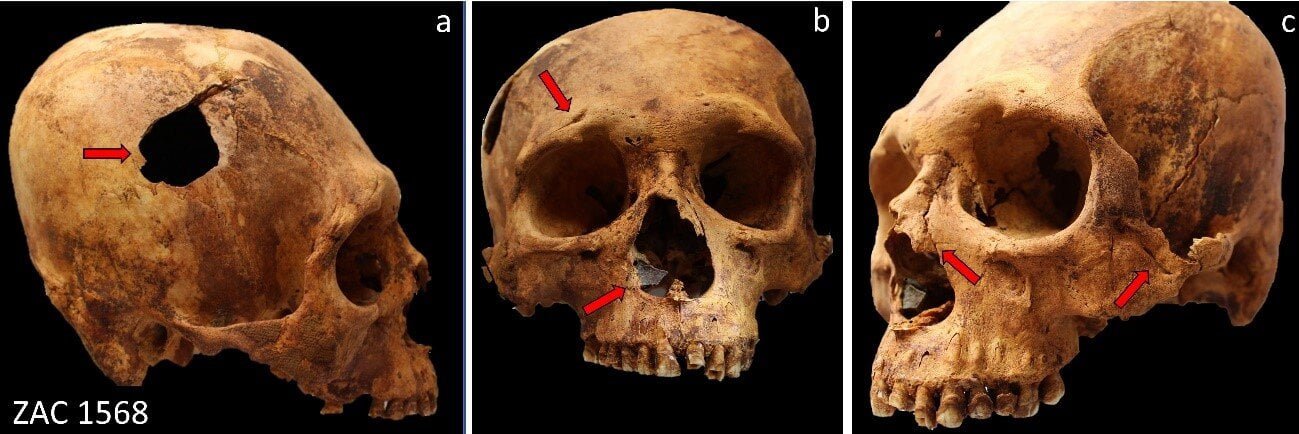 Various traumatic injuries in one of the individuals studied. Credit: Luis Pezo-Lanfranco
Various traumatic injuries in one of the individuals studied. Credit: Luis Pezo-Lanfranco
Pezo-Lanfranco suggests that these violent acts were likely perpetrated by outside groups, leading to intercommunity conflicts resulting in fatalities. Despite the brutality of these events, the victims were buried with customary funeral rites, indicating a continuation of community and care amidst turmoil.
The findings also unveil high levels of stress, infectious diseases, and material poverty among these ancient communities. The simplicity of grave goods and the prevalence of staple crops as the basis for subsistence further underscored the challenges faced by these societies.
The study also provided insights into the decline of the Chavín culture, a once-dominant civilization known for its monumental ceremonial centers like Chavín de Huantar. As this culture waned, possibly around 500-400 BCE, its religiously centered political structures gave way to more secular forms of governance, contributing to the region’s political disintegration.
The worship of a man-jaguar deity by the Chavín people, symbolizing the fusion of human and animal attributes, reflects rich spiritual traditions, though many aspects remain shrouded in mystery due to the absence of written records from this era.
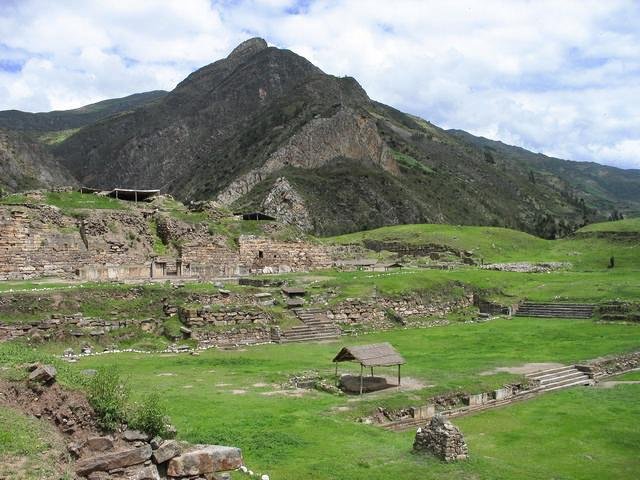 Detail of the Chavín de Huantar archeological site in Peru’s northern mountains. Credit: Sharon odb/Wikimedia Commons
Detail of the Chavín de Huantar archeological site in Peru’s northern mountains. Credit: Sharon odb/Wikimedia Commons
Pezo-Lanfranco emphasized the importance of this research in understanding a poorly documented chapter of Andean history, highlighting the complexities of societal changes, conflict, and the human condition during this pivotal period.
The study contributes not only to the understanding of the bioarchaeology of violence but also to broader insights into societal pressures and transitions shaping ancient Central Andean civilizations.
The study was published in the journal Latin American Antiquity.
More information: Pezo-Lanfranco L, Romero MIB, Filippini J, et al. (2024). Bioarchaeological Evidence of Violence between the Middle and Late Formative (500–400 BC) in the Peruvian North-Central Coast. Latin American Antiquity:1-17. doi:10.1017/laq.2023.38





