A new study published in the Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage has unveiled a captivating link between the ancient Egyptian sky goddess Nut and our galaxy, the Milky Way.
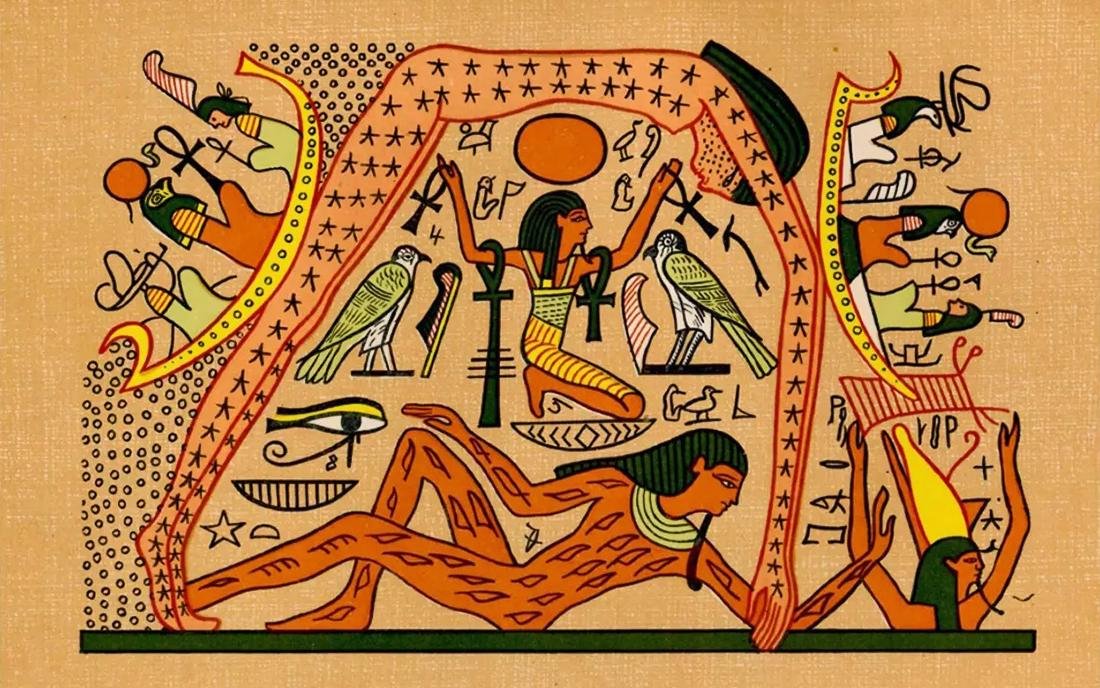 The sky goddess Nut, covered in stars, is held aloft by her father, Shu, and is arched over Geb, her brother the Earth god. On the left, the rising sun (the falcon-headed god Re) sails up Nut’s legs. On the right, the setting sun sails down her arms towards the outstretched arms of Osiris, who will regenerate the sun in the netherworld during the night. Credit: E. A. Wallis Budge, The Gods of the Egyptians, Vol. 2 (Methuen & Co., 1904).
The sky goddess Nut, covered in stars, is held aloft by her father, Shu, and is arched over Geb, her brother the Earth god. On the left, the rising sun (the falcon-headed god Re) sails up Nut’s legs. On the right, the setting sun sails down her arms towards the outstretched arms of Osiris, who will regenerate the sun in the netherworld during the night. Credit: E. A. Wallis Budge, The Gods of the Egyptians, Vol. 2 (Methuen & Co., 1904).
Ancient Egyptian civilization, renowned for its keen observations of the celestial realm, intertwined astronomical phenomena seamlessly into their religious narratives, mythology, and timekeeping practices. While their reverence for the Sun, Moon, and planets is well-documented, the role of the Milky Way in Egyptian culture has long remained elusive.
Drawing upon a diverse array of ancient Egyptian texts such as the Pyramid Texts, Coffin Texts, and the Book of Nut, alongside advanced astronomical simulations, the study presents a compelling argument that Nut, the celestial goddess of the sky, stars, and the universe, served as a symbolic representation of the Milky Way.
Nut, often depicted as a star-adorned woman arching over her brother Geb, the earth god, played a pivotal role in Egyptian cosmology. She safeguarded the earth from the encroaching void and orchestrated the solar cycle, symbolically swallowing the Sun at dusk and giving birth to it at dawn. While ancient texts and archaeological evidence have long showcased the Egyptians’ adeptness at observing celestial bodies, the precise role of the Milky Way in their religious worldview remained elusive.
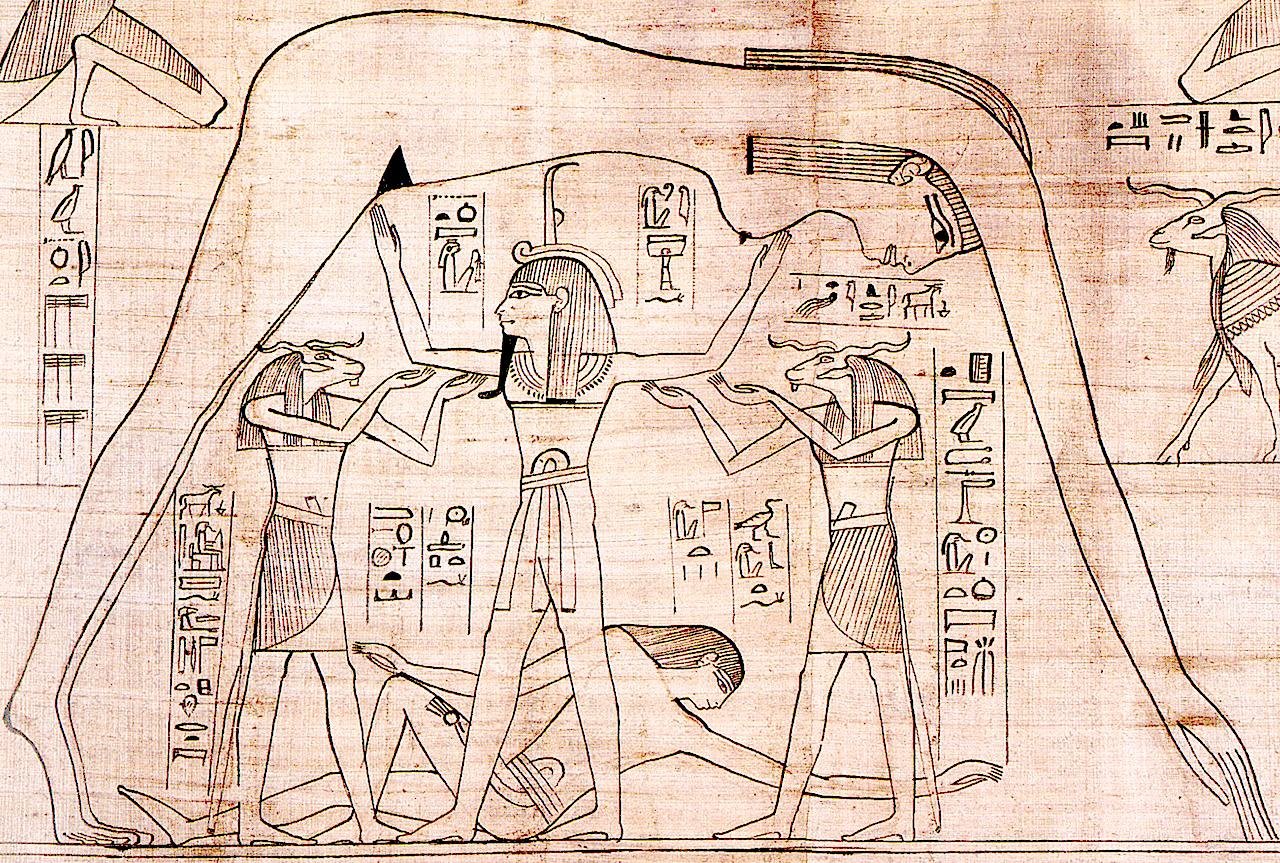 Detail from the Greenfield Papyrus (the Book of the ᴅᴇᴀᴅ of Nesitanebtashru). It depicts the air god Shu, ᴀssisted by the ram-headed Heh deities, supporting the sky goddess Nut as the earth god Geb reclines beneath. c. 950 BCE. Credit: What Life Was Like on the Banks of the Nile, edited by Denise Dersin, pH๏τographed by the British Museum/Wikipedia
Detail from the Greenfield Papyrus (the Book of the ᴅᴇᴀᴅ of Nesitanebtashru). It depicts the air god Shu, ᴀssisted by the ram-headed Heh deities, supporting the sky goddess Nut as the earth god Geb reclines beneath. c. 950 BCE. Credit: What Life Was Like on the Banks of the Nile, edited by Denise Dersin, pH๏τographed by the British Museum/Wikipedia
The study posits that during winter, the Milky Way illuminated Nut’s outstretched arms, while in summer, it traced her backbone across the heavens. This celestial choreography, echoing the cyclical rhythm of the seasons, underscored Nut’s divine presence in the night sky.
Dr. Graur’s exploration into the multifaceted symbolism of Nut extends beyond the boundaries of ancient Egypt, revealing striking parallels with diverse cultural interpretations of the Milky Way. Notably, Nut’s role in guiding the departed souls to the afterlife and her ᴀssociation with annual bird migrations resonate with analogous motifs found in North and Central American indigenous beliefs, as well as in Finnish and Baltic folklore.
By bridging the realms of astrophysics and Egyptology, this research marks a crucial step towards cataloging and studying the multicultural mythology of the Milky Way.
More information: Graur, O. (2024). The ancient Egyptian personification of the milky way as the sky-goddess nut: An astronomical and cross-cultural analysis. Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage, 27(1), 28–45. doi:10.3724/sp.j.1440-2807.2024.01.02





