Archaeologists have unearthed the skeleton of an adult male lynx accompanied by four dogs in a large pit from the Migration Period at the Zamárdi–Kútvölgyi-dűlő II site in Hungary.
 Archaeologists have unearthed the skeleton of a lynx accompanied by 4 big dogs in in Hungary. Credit: David Selbert
Archaeologists have unearthed the skeleton of a lynx accompanied by 4 big dogs in in Hungary. Credit: David Selbert
This discovery, detailed in a recent study published in the International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, marks the first complete archaeological lynx skeleton ever found in Europe.
The site, situated on the southern shore of Lake Balaton, was once part of the Roman provinces of Pannonia Prima and Valeria. As the Roman Empire declined, Germanic tribes such as the Lombards settled in the area. The burial’s dating of 430-550 CE coincides with the Lombards’ presence, suggesting a connection to their occupation.
The arrangement of the animals within the pit is peculiar. The lynx, a solitary and elusive creature, was positioned at the bottom, while the four dogs, roughly the size of modern German shepherds, were layered on top. Each animal was separated by layers of soil, indicating simultaneous or closely timed burials. However, the lack of a clear pattern in their arrangement leaves archaeologists questioning the purpose behind the burial.
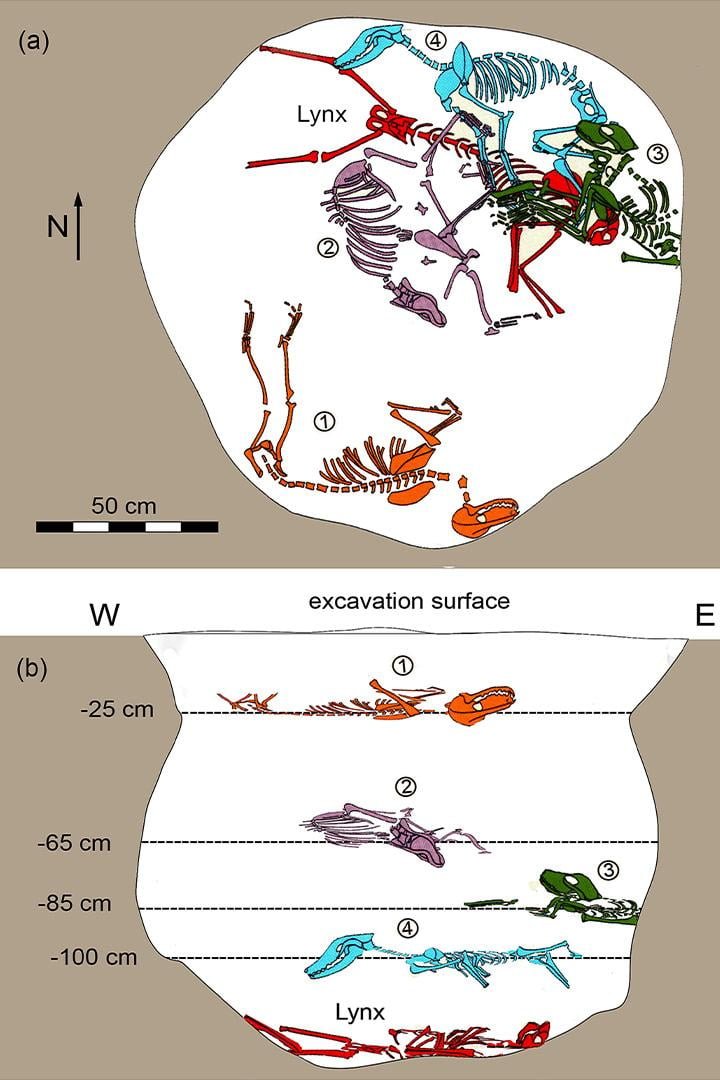 An illustration showing the the placement of the lynx skeleton (in red) and the four dog skeletons (purple, green, blue and orange) in the pit at the site in Hungary. Credit: Gál et al; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
An illustration showing the the placement of the lynx skeleton (in red) and the four dog skeletons (purple, green, blue and orange) in the pit at the site in Hungary. Credit: Gál et al; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Speculations abound regarding the nature of this unique deposit. Some suggest practical reasons, such as the possibility of a hunting accident or vermin control, while others lean towards ritualistic interpretations. Despite the absence of ritualistic symbols or evidence, the presence of such an unusual arrangement hints at the potential for ritual significance.
Lászlo Bartosiewicz, an archaeologist from Stockholm University involved in the study, told Live Science that “It is hard to summarize our interpretation…as no parallels…are known.” He emphasizes the complexity of the historical context, with the Migration Period representing a time of cultural upheaval and transformation.
Victoria Moses, a zooarchaeologist at Harvard University, acknowledged the difficulty in interpreting the burial’s significance, stating that while evidence of ritualistic elements exists, it’s challenging to draw definitive conclusions without additional material or ethnographic evidence.
Despite their rarity in the archaeological record, lynxes have left an indelible mark on human culture, symbolized by their claws and pelts found in ancient artifacts and garments. The Eurasian lynx, revered for its majestic presence, likely held significance in the cultural landscape of the region.
More information: Gál, E., Bartosiewicz, L., Kiss, V., Horváth, F., & Melis, E. (2024). A fifth‐ to sixth‐century CE lynx (Lynx lynx L., 1758) skeleton from Hungary 2: Stature and archaeological interpretations. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 34(2). doi:10.1002/oa.3289





