A recent study published in the journal Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences reveals significant findings from the examination of a late Roman shipwreck discovered off the coast of Mallorca, one of Spain’s Balearic Islands.
 Main types of amphorae documented at Ses Fontanelles shipwreck: DSF-179 and DSF-189, Almagro 51c with тιтuli picti; DSF-266, Flat-bottom amphora; DSF-002, Ses Fontanelles I type. Credit: M.A. Cau-Ontiveros et al. Archaeol Anthropol Sci (2024)
Main types of amphorae documented at Ses Fontanelles shipwreck: DSF-179 and DSF-189, Almagro 51c with тιтuli picti; DSF-266, Flat-bottom amphora; DSF-002, Ses Fontanelles I type. Credit: M.A. Cau-Ontiveros et al. Archaeol Anthropol Sci (2024)
This shipwreck, located just 65 meters from a popular tourist beach near Palma, the capital of Mallorca, has drawn attention for its exceptional preservation and intriguing cargo.
The research, conducted by a team of archaeologists and researchers, employed a comprehensive analytical approach to unravel the mysteries surrounding the origin, contents, and significance of the shipwreck. Combining petrographic analysis, archaeozoology, residue analysis, and the study of wood and plant remains, the team embarked on a thorough investigation.
The cargo hold of the vessel revealed an ᴀssortment of ceramic artifacts, predominantly amphorae, used for storing and transporting various goods. One of the key findings of the study is the identification of a new type of amphora, named Ses Fontanelles I, which was found exclusively in this wreck. Remarkably larger and heavier than its counterparts, this newly identified amphora was primarily utilized for carrying plant oil.
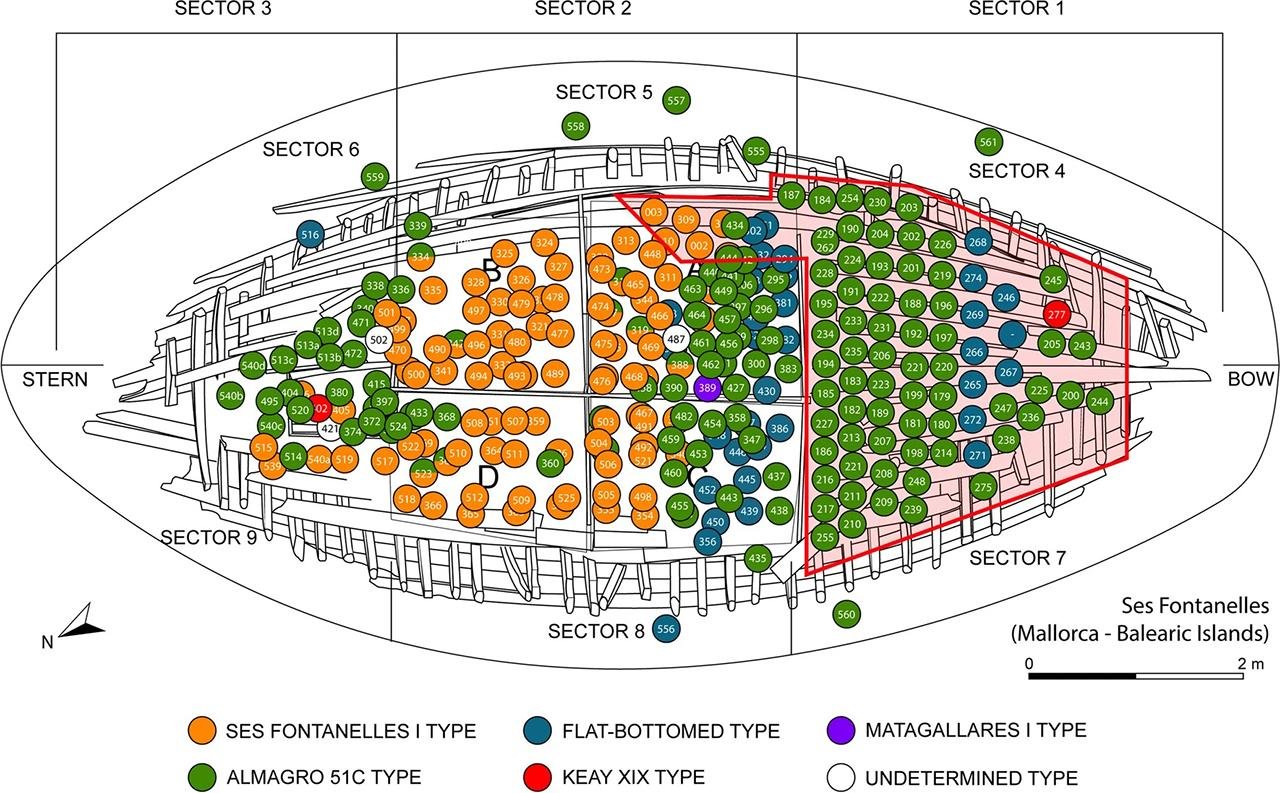 Plan of the wreck with the position of the cargo amphorae documented during the excavation process. Credit: M.A. Cau-Ontiveros et al. Archaeol Anthropol Sci (2024)
Plan of the wreck with the position of the cargo amphorae documented during the excavation process. Credit: M.A. Cau-Ontiveros et al. Archaeol Anthropol Sci (2024)
The amphorae recovered from the wreck bear painted inscriptions known as тιтuli picti, which provide valuable information about the origin, contents, and ownership of the cargo. The inscriptions identify the manufacturers of the amphorae as Ausonius et Alunni, and reveal that the cargo included fish sauce, olive oil, and wine.
Fish sauce, known as liquamen flos, was a popular condiment during the Late Roman period, distinct from the ubiquitous garum. The analysis suggests that the fish sauce was primarily made from anchovies (Engraulis encrasicolus), with occasional sardines.
Furthermore, residue analysis of the amphorae indicated the presence of grape derivatives, possibly used as a condiment or preservative, along with traces of animal products, reinforcing the complexity of the cargo composition.
The hull’s construction materials, meticulously examined, revealed a strategic selection of forest resources. Analysis of the wood used in the hull revealed a careful selection of materials, with pine employed for longitudinal elements and harder woods such as juniper, olive, and laurel used for ᴀssembly components. Vine branches and other herbaceous plants were utilized as filler and cargo protection during the voyage.
The research suggests that the ship likely departed from the area of Cartagena in southeastern Spain, navigating the trade routes of the western Mediterranean. This conclusion is supported by the petrographic analysis of the amphorae, which indicates a connection to the Cartagena region.
More information: Cau-Ontiveros, M.Á., Bernal-Casasola, D., Pecci, A. et al. (2024). Multianalytical approach to the exceptional Late Roman shipwreck of Ses Fontanelles (Mallorca, Balearic Islands, Spain). Archaeol Anthropol Sci 16, 58. doi:10.1007/s12520-024-01952-3





