In a recent study published in the journal Frontiers in Medicine, researchers have unveiled evidence suggesting that ancient Egyptians, more than 4,000 years ago, may have attempted to treat cancer through surgical interventions.
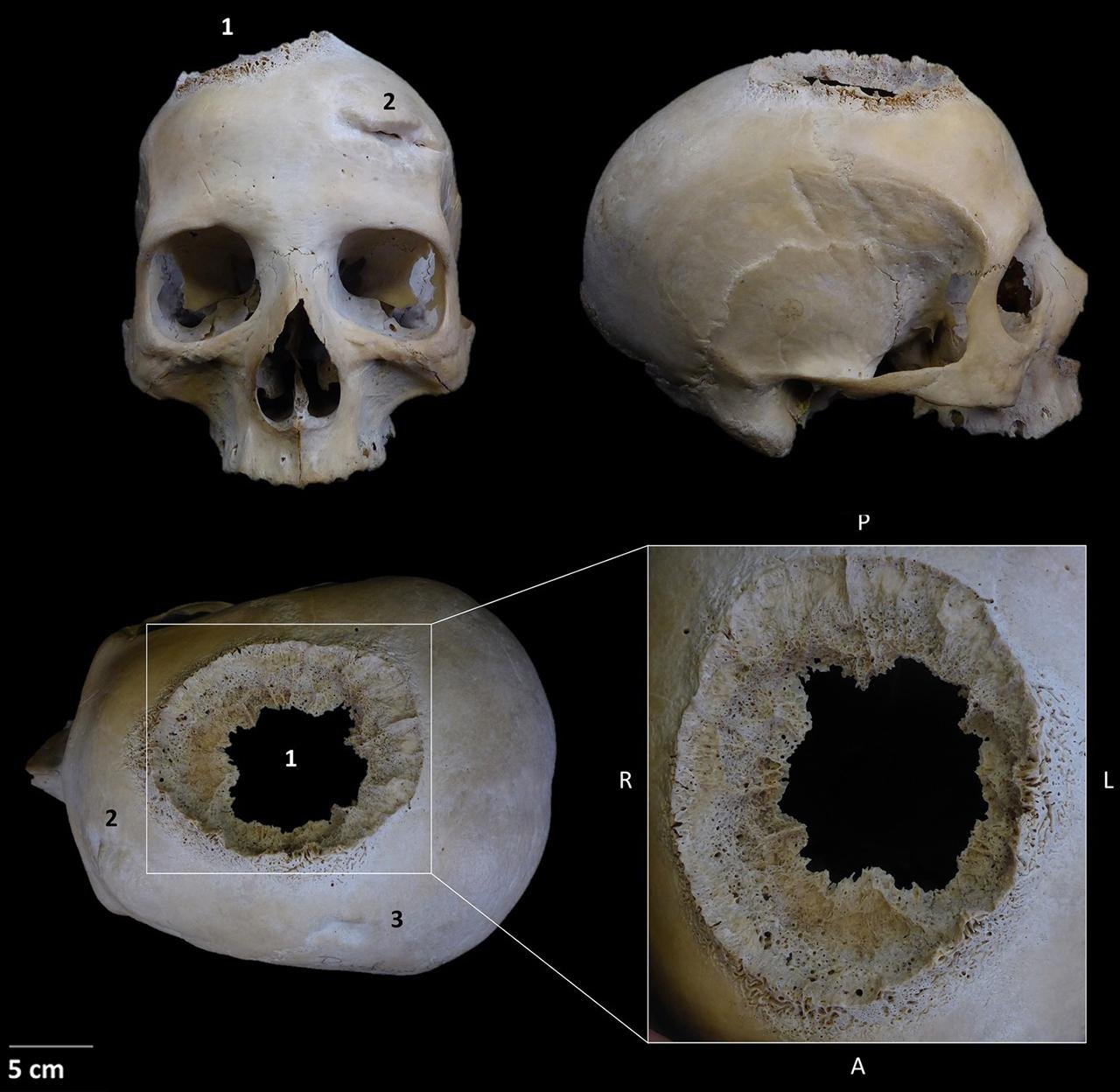 Skull E270: Frontal position showing the three lesions, right lateral view; and detail of the neoplastic lesion identified. Credit: Tatiana Tondini et al. Frontiers in Medicine (2024)
Skull E270: Frontal position showing the three lesions, right lateral view; and detail of the neoplastic lesion identified. Credit: Tatiana Tondini et al. Frontiers in Medicine (2024)
The study, led by an international team of researchers, focused on two skulls dating back to ancient Egypt. One skull, belonging to a male aged 30 to 35, showed evidence of a large primary tumor and over 30 smaller metastatic lesions.
Microscopic analysis revealed cut marks around these lesions, indicating attempts at surgical intervention. This finding suggests that ancient Egyptians may have sought to remove cancerous growths, pushing back the timeline of surgical cancer treatment by millennia.
“This is where modern medicine starts,” remarked Edgard Camarós Perez, a paleopathologist involved in the study. The discovery challenges the notion that cancer was solely a disease of the modern age. It highlights the sophistication of ancient Egyptian medicine, which encompᴀssed not only herbal remedies but also surgical practices.
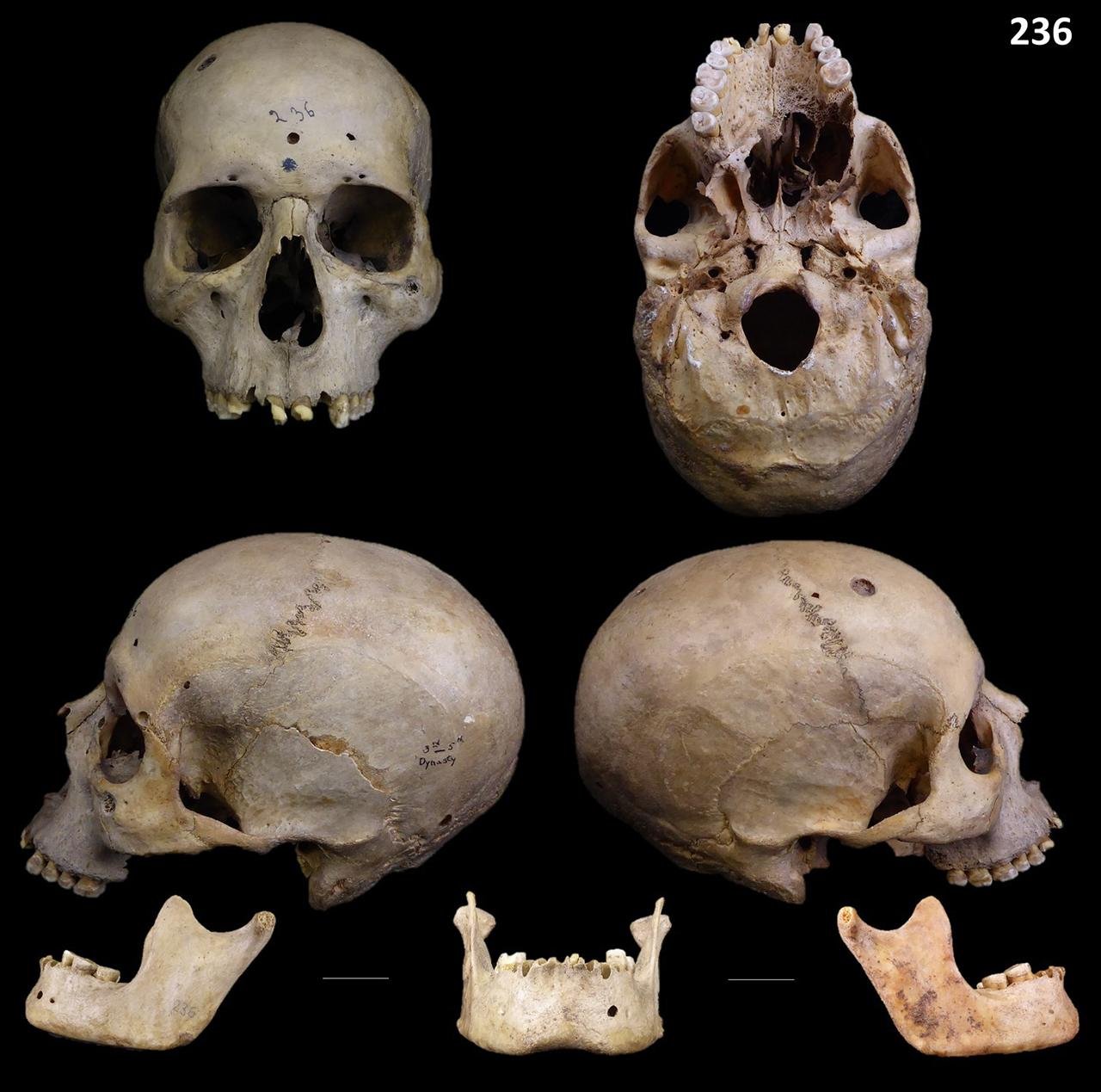 Skull 236: Frontal view; inferior view, left and right lateral view and mandible. Credit: Tatiana Tondini et al. Frontiers in Medicine (2024)
Skull 236: Frontal view; inferior view, left and right lateral view and mandible. Credit: Tatiana Tondini et al. Frontiers in Medicine (2024)
The researchers also examined the skull of a woman who lived between 664 and 343 BCE and was 50 years old at the time of her death. This skull, housed within the University of Cambridge’s Duckworth Collection, exhibited signs of cancerous tumors, along with evidence of successful treatment for traumatic injuries. This suggests that while ancient Egyptians were capable of treating certain conditions, they faced challenges in combating cancer.
The presence of perimortem cut marks around the cancerous lesions raises questions about whether the surgeries were performed while the patients were alive or as part of postmortem examinations.
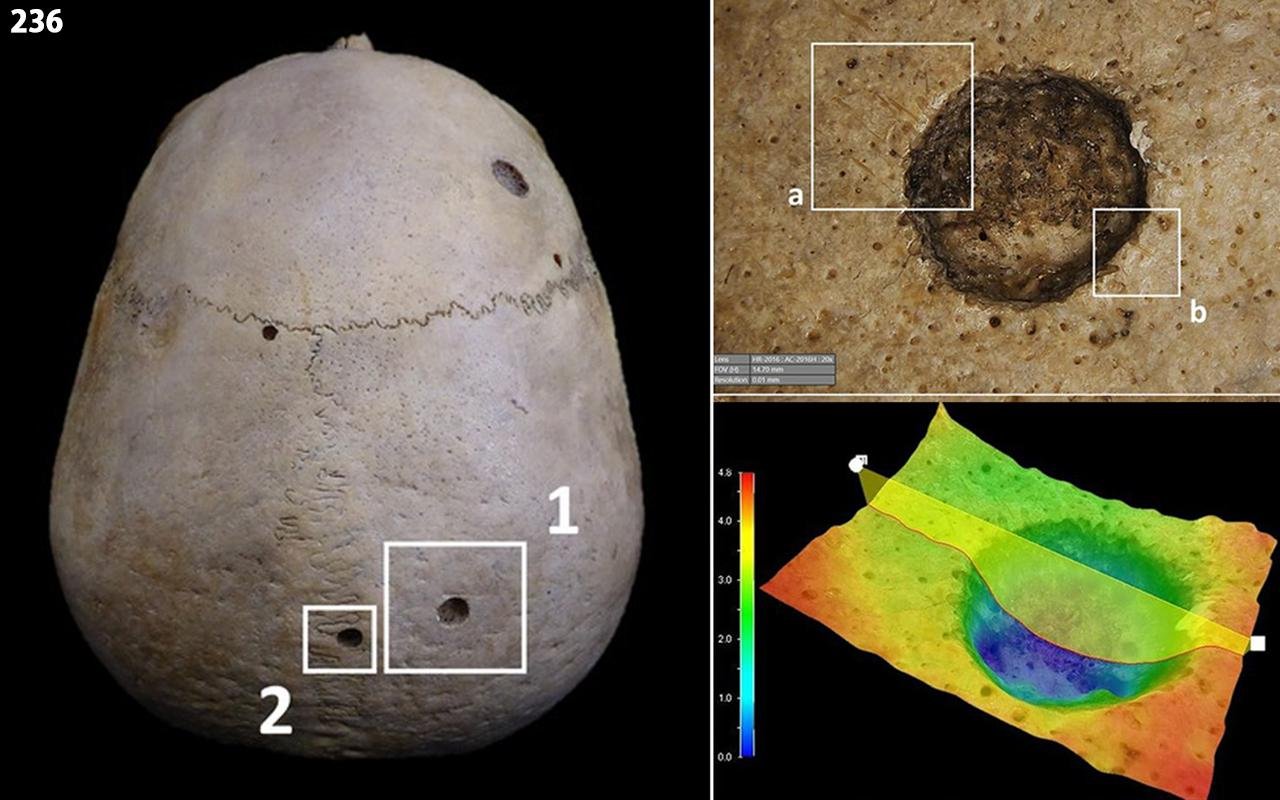 Images of the cut marks close to the two lesions taken with the HIROX Microscope. Credit: Tatiana Tondini et al. Frontiers in Medicine (2024)
Images of the cut marks close to the two lesions taken with the HIROX Microscope. Credit: Tatiana Tondini et al. Frontiers in Medicine (2024)
Dr. Ibrahem Badr, an ᴀssociate professor specializing in ancient Egyptian medicine, noted that while ancient Egyptian medicine was extensively documented, modern technologies are uncovering new insights into its practices.
The research adds a chapter to the “obscure biography” of cancer. By utilizing modern methodologies, such as micro-CT scanning and microscopic analysis, the researchers hope to gain a more comprehensive understanding of ancient Egyptian medicine.
More information: Tondini T, Isidro A and Camarós E (2024) Case report: Boundaries of oncological and traumatological medical care in ancient Egypt: new palaeopathological insights from two human skulls. Front. Med. 11:1371645. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1371645





