Researchers have unveiled remarkable details about a mummified crocodile by using 3D imaging technology to piece together the life and death of the crocodile, mummified by the ancient Egyptians.
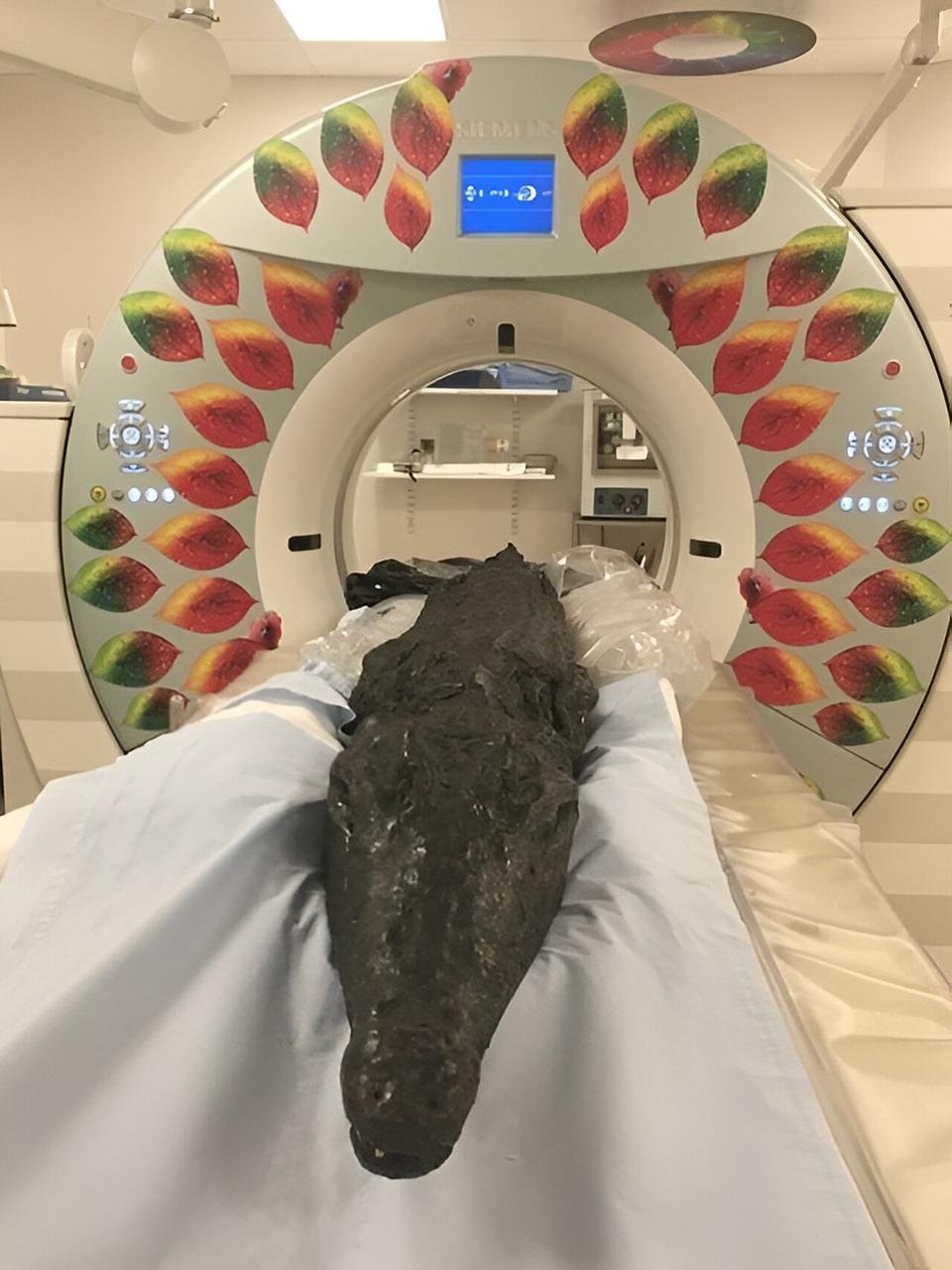 Crocodile in the CT scanner. Credit: University of Manchester
Crocodile in the CT scanner. Credit: University of Manchester
The crocodile, which measures approximately 2.2 meters (7.2 feet) in length, has been the subject of intense study using state-of-the-art 3D imaging technology. The findings were published in the journal Digital Applications in Archaeology and Cultural Heritage.
The mummified crocodile, identified as specimen 2005.335, is housed at the Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery in the UK. Researchers from The University of Manchester, Loughborough University, and Birmingham City University collaborated on the project, which involved X-ray and CT scanning to examine the crocodile’s internal structure without causing any damage.
One of the most striking discoveries was the presence of a freshly eaten fish, still attached to a bronze hook, inside the crocodile’s stomach. This discovery suggests that the crocodile was wild-caught and died shortly after ingesting the baited fish. Dr. Lidija McKnight, lead author and Research Fellow from The University of Manchester explained to Newsweek, “The presence of the hook and the fish suggests that the [crocodile] died soon after ingesting them due to the lack of degradation by the digestive enzymes.”
The researchers also noted that the crocodile had swallowed numerous small stones, known as gastroliths, which these animals ingest to help break down food and regulate buoyancy. The placement of the gastroliths higher up in the digestive tract indicated an attempt to process the crocodile’s last meal before death. This further supports the theory that the animal died soon after consuming the fish.
The study also explored the cultural and religious significance of crocodiles in ancient Egypt. These animals were venerated as symbols of fertility, ᴀssociated with the annual Nile inundation and the resulting fertile agricultural land. They were also linked to the god Sobek, who was believed to embody the power and ferocity of the crocodile. Crocodiles were often mummified as offerings to Sobek, and this particular specimen is believed to have been prepared for such a purpose.
Dr. McKnight said: “Mummies have long been a source of fascination for museum visitors of all ages. Our work provides a unique opportunity to connect visitors to the story of this animal.” She emphasized the advantages of non-invasive techniques such as 3D radiography over traditional methods like unwrapping and autopsy, which can damage the specimens.
The meticulous scientific analysis also involved the virtual extraction of the fish hook from the mummy. Using specialist software, the researchers created a plastic replica of the hook, which was then cast in bronze, the material of the original hook. This process illustrated the advanced metallurgical techniques used by the ancient Egyptians, who likely employed hardened clay molds and charcoal-based heat sources to produce such items.
The study also revealed much about ancient Egyptian beliefs and practices. Some crocodiles, like the famous Suchus at the cult center of Crocodilopolis, were pampered as “cult animals,” receiving lavish diets and adornments befitting their divine status. Others were captured from the wild, possibly using baited hooks, and mummified as offerings. Dr. McKnight added: “Our work revealed a great amount of information, both about the life of the crocodile and the post-mortem treatment of its remains.”
University of Manchester
More information: McKnight, L. M., Bibb, R., & Cooper, F. (2024). Seeing is believing – The application of Three-Dimensional modelling technologies to reconstruct the final hours in the life of an ancient Egyptian Crocodile. Digital Applications in Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, 34(e00356), e00356. doi:10.1016/j.daach.2024.e00356





