The catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE, which led to the complete burial of the ancient Roman city of Pompeii under volcanic ash, is well-documented. Recent research, however, reveals that a simultaneous earthquake played a significant role in the city’s destruction and the death of its inhabitants.
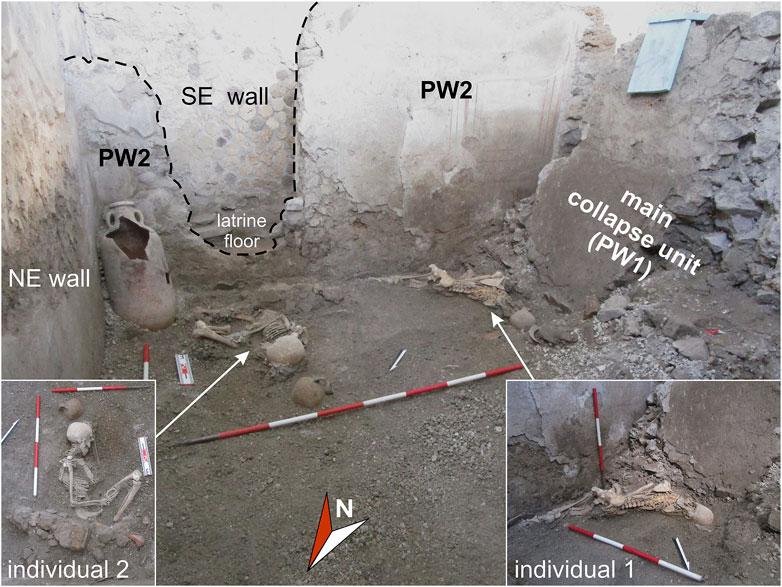 View from the north of the northern sector of room A during the excavation. The skeletons of two individuals lay in the south-western (individual 1) and south-eastern corner (individual 2). Credit: Sparice et al., Frontiers in Earth Science (2024)
View from the north of the northern sector of room A during the excavation. The skeletons of two individuals lay in the south-western (individual 1) and south-eastern corner (individual 2). Credit: Sparice et al., Frontiers in Earth Science (2024)
Published in the journal Frontiers in Earth Science, this study offers compelling evidence that seismic activity occurred concurrently with the volcanic eruption, leading to the collapse of buildings and additional fatalities. This new perspective challenges the long-standing belief that the majority of Pompeii’s residents died solely from the volcanic fallout.
The notion of seismic activity during Vesuvius’s eruption isn’t entirely new. Pliny the Younger, a Roman author who witnessed the event from a nearby town, described violent tremors accompanying the eruption in his letters. Despite his accounts, modern scholars had not found concrete evidence to support this until now.
Domenico Sparice, a volcanologist at Italy’s National Insтιтute of Geophysics and Volcanology and lead author of the study, explains that previous excavations in Pompeii lacked input from archaeoseismologists—experts who study the impact of earthquakes on ancient structures. By involving such specialists, the research team uncovered significant evidence of earthquake-induced damage.
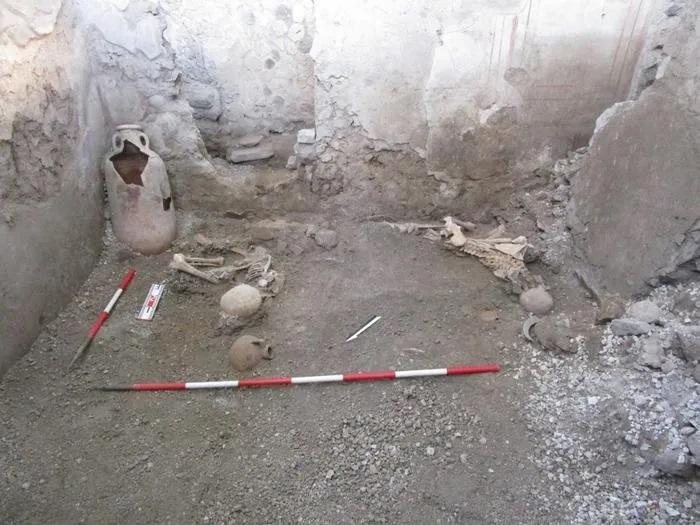 The remains of two people recently uncovered at Pompeii. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
The remains of two people recently uncovered at Pompeii. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
The team’s investigation centered on the Insula of the Chaste Lovers, a well-preserved area in Pompeii that includes a bakery and a house. Here, archaeologists discovered the skeletons of two men buried under collapsed walls. Their analysis revealed that these individuals likely died from injuries consistent with those caused by seismic activity.
One of the victims was found with over 20 rib fractures, crush injuries to the facial bones, pelvis, and limbs, indicating he was struck by a large falling wall. The other victim, buried up to his legs, had fewer fractures but was found in a defensive posture, suggesting an awareness of the impending collapse.
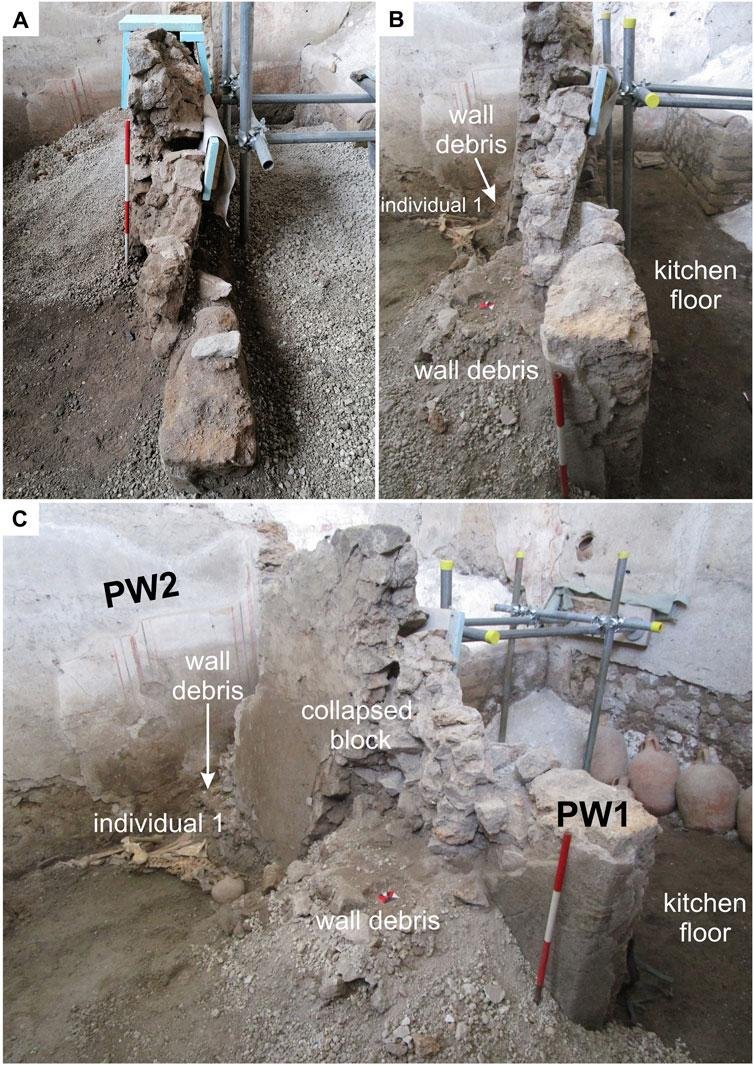 PH๏τographs of the major collapse unit in Pompei. Credit: Sparice et al., Frontiers in Earth Science (2024)
PH๏τographs of the major collapse unit in Pompei. Credit: Sparice et al., Frontiers in Earth Science (2024)
Dr. Sparice and his team ruled out volcanic debris as the cause of the wall’s collapse. Instead, they linked the destruction to seismic shocks, supported by stratigraphic and structural evidence from the site. This discovery aligns with modern earthquake trauma patterns, providing a new lens through which to view the disaster.
The findings propose an updated sequence of events for the 79 CE catastrophe. Initially, the city was bombarded with volcanic lapilli (small stones) for about 18 hours, causing many roofs to cave in. Following this, an earthquake—triggered by the ongoing eruption—shook the city, leading to further destruction and deaths. Finally, pyroclastic flows of ash and gas swept through Pompeii, sealing its fate.
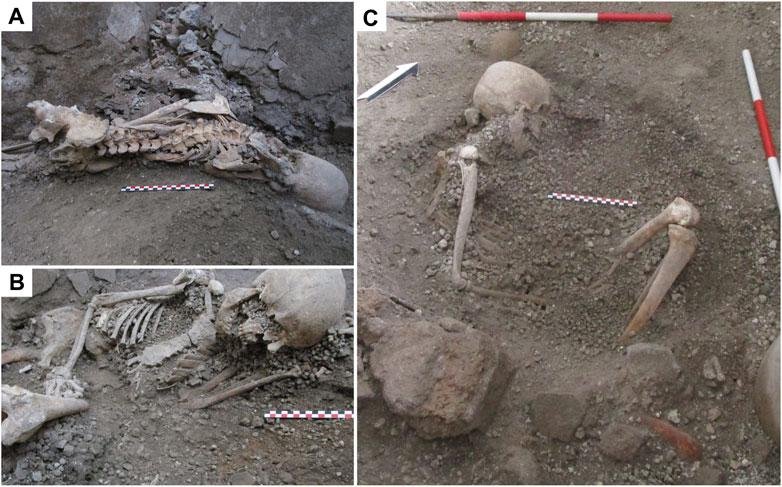 Details of the skeletons found in the northern sector of Room A. Credit: Sparice et al., Frontiers in Earth Science (2024)
Details of the skeletons found in the northern sector of Room A. Credit: Sparice et al., Frontiers in Earth Science (2024)
Dr. Sparice and his colleagues plan to extend their research to other areas within Pompeii, aiming to identify additional instances of earthquake-induced damage. This research also opens avenues for investigating the impact of seismic activity on other ancient cities affected by Vesuvius, such as Herculaneum and Stabiae.
More information: Sparice, D., Amoretti, V., Galadini, F., Di Vito, M. A., Terracciano, A., Scarpati, G., & Zuchtriegel, G. (2024). A novel view of the destruction of Pompeii during the 79 CE eruption of Vesuvius (Italy): syn-eruptive earthquakes as an additional cause of building collapse and deaths. Frontiers in Earth Science, 12. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1386960





