Researchers from the State Office for Monument Preservation and Archaeology (LDA) of Saxony-Anhalt have uncovered a significant Slavic settlement and burial ground near Wettin-Löbejün, Germany.
 The archaeological site at Wettin-Löbejün, Germany. Credit: Oliver Dietrich, State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt
The archaeological site at Wettin-Löbejün, Germany. Credit: Oliver Dietrich, State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt
This discovery was made during preparatory work for the SuedOstLink, a major 170-kilometer underground powerline project stretching from Wolmirstedt in Saxony-Anhalt to Landshut in Bavaria.
The excavations have revealed a settlement spanning 1.2 acres, dating back to the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (5th to 10th century CE). This area demonstrates two distinct phases of occupation.
The earlier phase featured a fortified enclosure with a four-meter-wide defensive ditch, while the later phase saw the establishment of individual farmsteads surrounded by smaller, 0.5-meter-wide ditches. Significant artifacts, such as a pearl and a bronze bracelet, were found in these ditches.
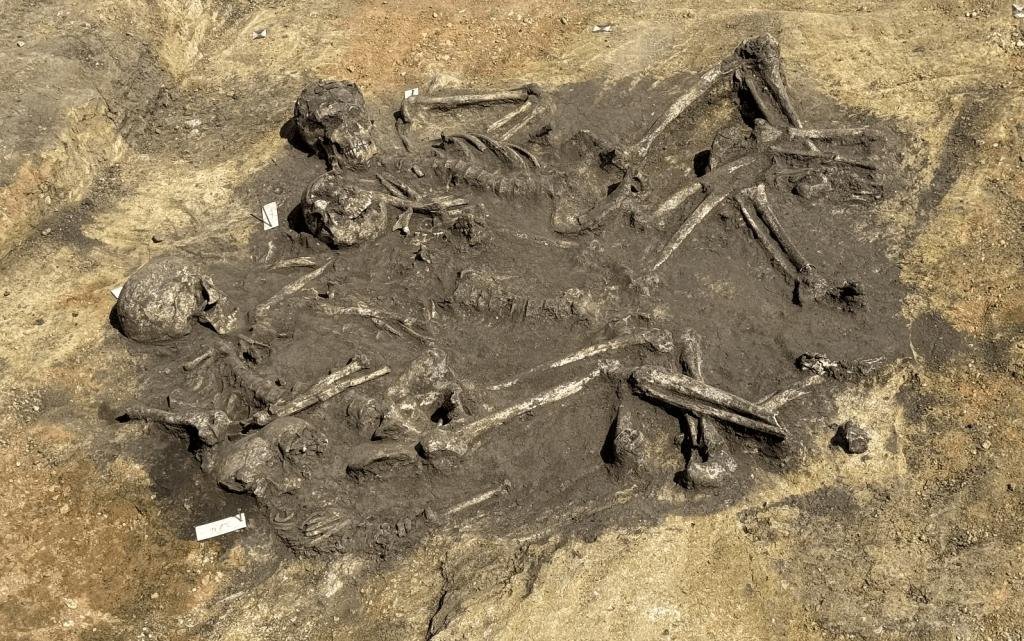 ‘Family grave’ of two adults and two children from Wettin-Löbejün. Credit: Oliver Dietrich, State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt
‘Family grave’ of two adults and two children from Wettin-Löbejün. Credit: Oliver Dietrich, State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt
A notable aspect of the settlement is a craftsmen’s quarter, which includes pits used for extracting bog iron ore and a blast furnace for on-site processing. Evidence of textile production has also been uncovered, indicated by finds of spindle whorls. Two wells, each approximately 1.5 meters deep, provided water to the inhabitants.
Adjacent to the settlement, a burial ground has been completely excavated, revealing around 60 graves aligned in two parallel rows. The graves, mostly dating to the 10th and 11th centuries CE, adhered to Christian burial rites, with the deceased laid on their backs facing east.
These burials were characterized by head niches, a common feature from the late 10th to the 12th century. According to the LDA, the cemetery measured a modest 5 by 30 meters and contained burials without grave goods except for items belonging to garments, such as bronze rings and beads.
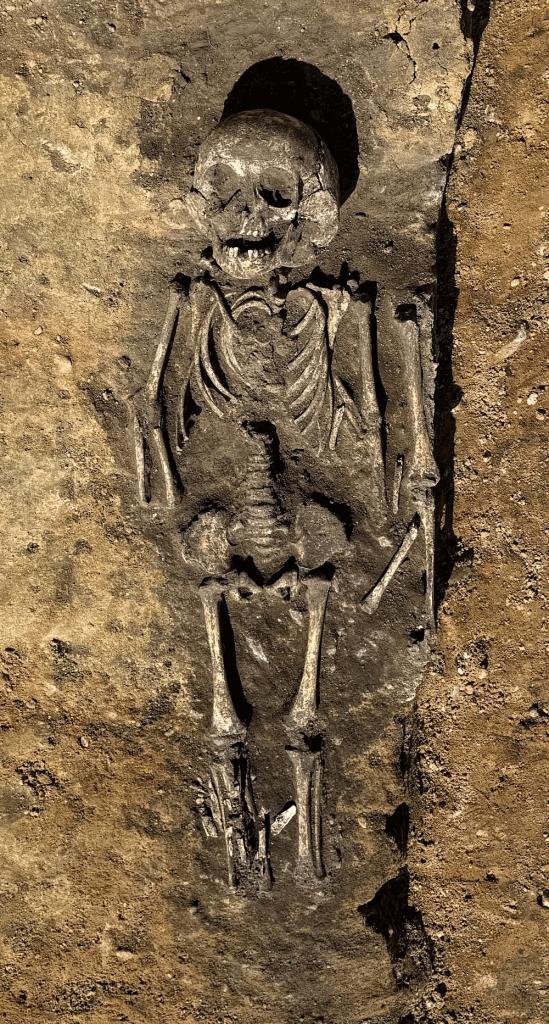 Grave of a child with ‘hydrocephalus’ from Wettin-Löbejün. Credit: Oliver Dietrich, State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt
Grave of a child with ‘hydrocephalus’ from Wettin-Löbejün. Credit: Oliver Dietrich, State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt
Among the burials, two findings stand out. A family grave containing the remains of two adults and two children was discovered, with traces of wooden corner posts and beams suggesting a complex grave architecture.
Additionally, the burial of a child who likely suffered from hydrocephalus—a condition causing excessive cerebrospinal fluid to accumulate in the skull—was found. This child’s grave included beads placed in the chest area, indicating the community’s special concern.
Excavations near Wettin-Löbejün began at the end of 2023, with work continuing intermittently due to harsh weather conditions. Currently, 20 employees are examining the site. The archaeological work in this area is expected to be completed by the end of August 2024.
State Office for Monument Preservation and Archaeology (LDA) of Saxony-Anhalt





