Archaeologists in Germany have uncovered one of the largest medieval coin hoards in recent decades during a routine construction project in the village of Glottertal, situated in the picturesque Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald district. The find, consisting of around 1,600 silver coins, dates back to the early 14th century.
 Some of the 1,500 silver coins discovered in Germany. Credit: Courtesy of the State Office for Monument Preservation in the Stuttgart Regional Council
Some of the 1,500 silver coins discovered in Germany. Credit: Courtesy of the State Office for Monument Preservation in the Stuttgart Regional Council
The discovery was made in early May 2024 when Claus Völker, a local resident ᴀssisting with the installation of a water pipeline near a village swimming pool, noticed what he initially thought were “small metal plates” among the excavated soil. Recognizing their potential importance, Völker promptly reported the find to the State Office for Monument Preservation (LAD) in the Stuttgart Regional Council.
Responding to the report, LAD archaeologist Andreas Haasis-Berner and his team arrived on-site the same day to investigate further. They quickly unearthed an initial 1,000 coins, halting the construction project to allow for a more thorough archaeological inspection. Despite the challenging conditions—heavy rains had turned the trench into a knee-deep quagmire—the team, aided by three licensed metal detectorists, managed to recover an additional 600 coins, bringing the total count to approximately 1,600.
The hoard primarily consists of coins minted around 1320 from various mints in what are now Germany, Switzerland, and France. According to Haasis-Berner, the majority of the coins originated from mints in Breisach, Zofingen, and Freiburg, with a smaller number from Basel, St. Gallen, Zurich, Laufenburg, and Colmar. This diverse array of coins underscores the extensive trade networks and currency circulation within the region during the early 14th century.
 A close-up of one of the silver coins discovered in Glottertal, Germany. Credit: Courtesy of the State Office for Monument Preservation in the Stuttgart Regional Council
A close-up of one of the silver coins discovered in Glottertal, Germany. Credit: Courtesy of the State Office for Monument Preservation in the Stuttgart Regional Council
As Haasis-Berner explained, the hoard is expected to provide valuable information about several aspects of the region’s history, including the circulation of coins in Breisgau, the minting activities of local mints, and the silver trade. Additionally, it may offer clues about mining operations in Glottertal, an area known for its silver mines during the Middle Ages.
The exact circumstances surrounding the burial of the coins remain unclear. They could have been hidden as a safeguard against theft or conflict, or perhaps as a way to preserve wealth. Haasis-Berner noted that at the time the coins were minted, they would have held significant purchasing power, with the value equivalent to about 150 sheep.
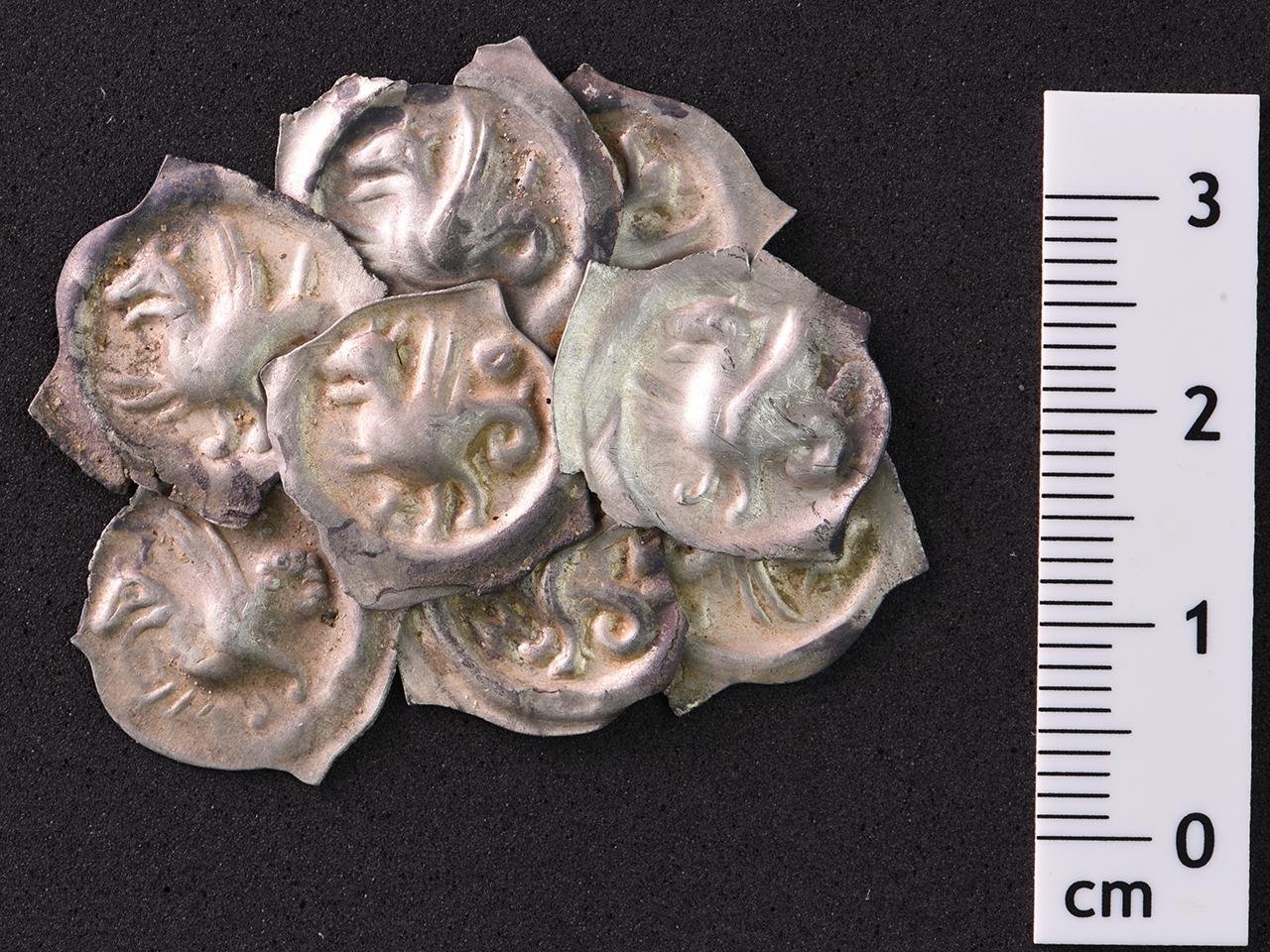 A selection of coins from the hoard after cleaning. Credit: Courtesy of the State Office for Monument Preservation in the Stuttgart Regional Council
A selection of coins from the hoard after cleaning. Credit: Courtesy of the State Office for Monument Preservation in the Stuttgart Regional Council
This discovery marks the largest medieval coin hoard found in the region since 1949, when archaeologists in Freiburg unearthed around 5,000 coins dating back to the 1280s. However, no similar finds had been made in Glottertal until now, making this a particularly noteworthy event for the area.
The coins are currently undergoing cleaning and conservation, and they are expected to be studied in greater detail over the coming months. Once fully documented, they will likely be displayed to the public.
Stuttgart Regional Council





