Archaeologists from the University of Stavanger’s Archaeological Museum have uncovered a remarkable Viking treasure hoard in the Hjelmeland municipality, Norway.
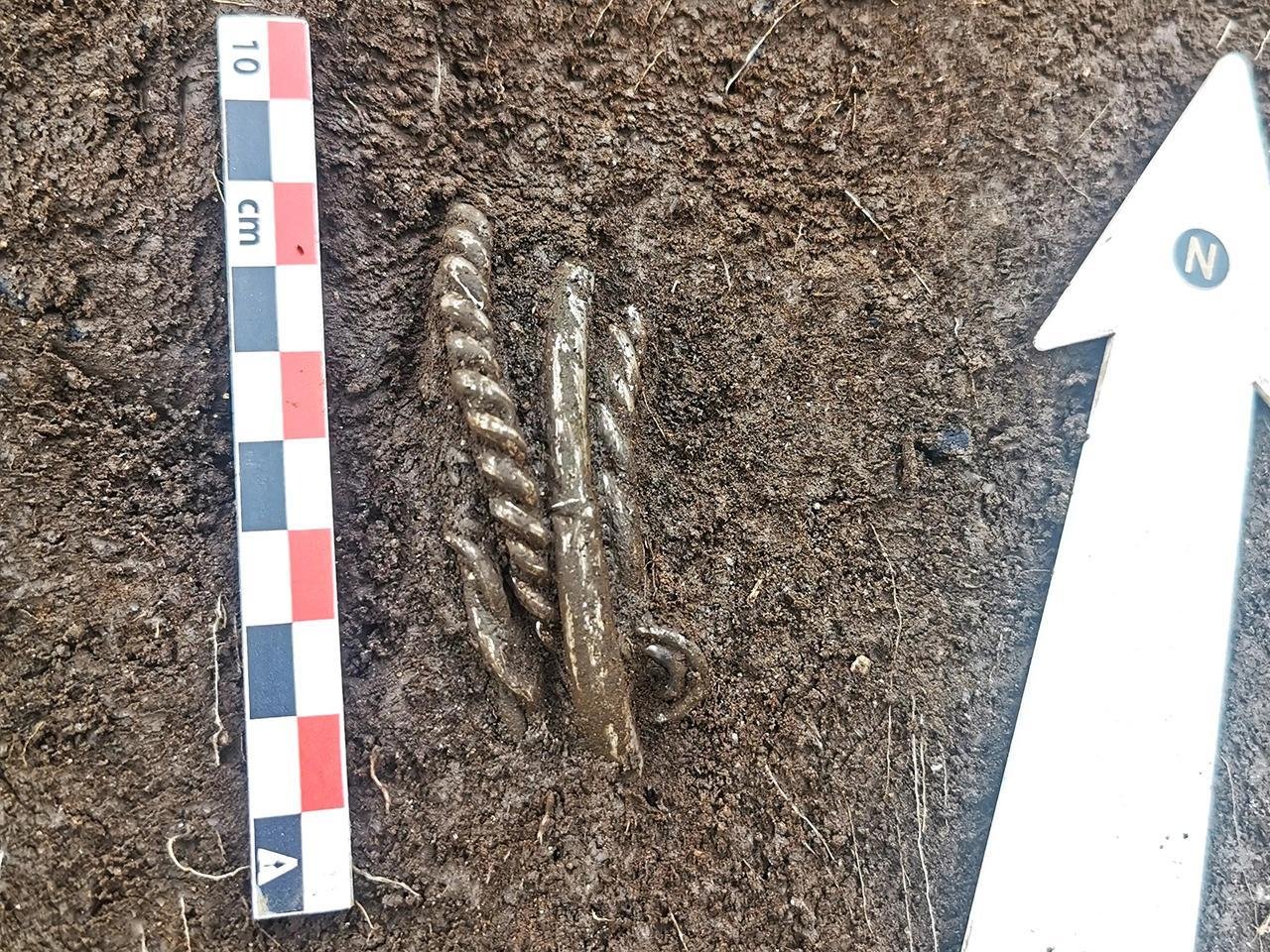 The silver treasure was discovered exactly where it had been buried by the Vikings centuries ago. Credit: Volker Demuth, Archaeological Museum, University of Stavanger
The silver treasure was discovered exactly where it had been buried by the Vikings centuries ago. Credit: Volker Demuth, Archaeological Museum, University of Stavanger
The discovery, made during excavations ahead of the construction of a new farm road, includes four silver bracelets, thought to be over 1,100 years old, buried under the floor of what is believed to be a slave dwelling on a Viking farm.
The excavation was initiated when local farmer Tårn Sigve Schmidt contacted the museum, asking archaeologists to survey the route of the planned road. Mari Krogstad Samuelsen and Ola Tengesdal Lygre, field archaeologists at the site, initially mistook the treasure for twisted copper wires, common in agricultural land. However, upon closer examination, they realized they had uncovered a set of intricately designed silver bangles. “When I saw there were several and they weren’t copper, but silver, I realized we had stumbled upon something significant,” Lygre said.
The bracelets were found just 20 centimeters below the surface, still in the exact location where they were buried during the 9th century. According to archaeologist and project manager Volker Demuth, this is a rare occurrence. “Usually, valuable objects like these are found in ploughed fields, where they’re displaced from their original context. Since this silver treasure hasn’t been moved, it offers us fresh insights into life and society during the Viking Age,” Demuth explained.
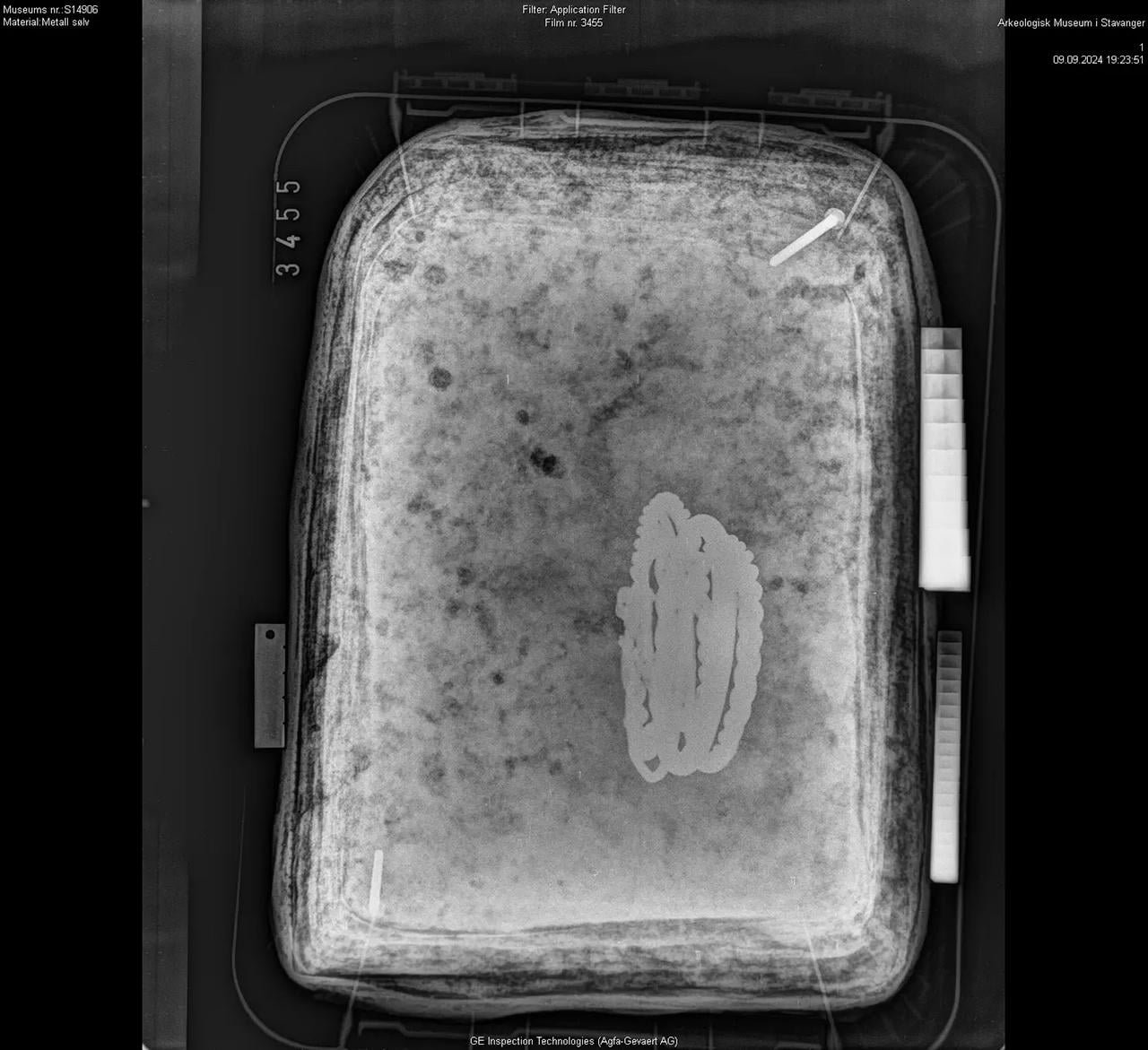 X-ray of the hoard in the soil block. Credit: Archaeological Museum, University of Stavanger
X-ray of the hoard in the soil block. Credit: Archaeological Museum, University of Stavanger
The Viking farm where the treasure was discovered included several structures, both for the inhabitants and their animals. Excavations revealed everyday items such as soapstone pots, knife blades, rivets, and whetstones, used for sharpening tools. This site, perched on a mountainside, likely allowed the Vikings control over access to the nearby fjord.
Archaeologists believe the bracelets were buried in haste as the farm was being abandoned, possibly during an attack. Evidence of burning suggests the farmstead was destroyed by fire around the same time, during a period of unrest in Norway. “If the residents of this farm had to flee from an attack, it would make sense for them to hide their valuables before escaping into the mountains,” said Demuth.
The silver hoard is thought to have come from abroad, as there were no active silver mines in Norway at the time. Vikings often acquired silver through trade, as gifts, or from raiding expeditions. These bracelets bear a striking resemblance to silver necklaces found in the same region in 1769, raising the possibility of a connection between the two finds, although this has not yet been confirmed.
While the exact reason for the burial remains unclear, some speculate it could be tied to Viking customs, where valuable items were sometimes buried to mark territory or in the belief they could be retrieved in the afterlife, as described in the Heimskringa saga. The saga records that, according to Odin’s Law, men were allowed to take with them to Valhalla anything they had personally buried.
The silver bracelets are now being studied at the Archaeological Museum of the University of Stavanger, where conservators are carefully examining the soil for traces of organic material, such as cloth or leather, that may have wrapped the treasure when it was buried. The hoard will be displayed at the museum once analysis and conservation work is complete.
Museum Director Ole Madsen said: “This is an absolutely fantastic find, which gives us completely unique knowledge about one of the most central eras in Norway, namely the Viking Age.”
Archaeological Museum at the University of Stavanger





