Archaeologists have unveiled a previously unknown Maya city and over 6,600 related structures hidden beneath the dense tropical forests of Campeche, Mexico.
 The city discovered in Campeche was hidden beside modern buildings and highways. Credit: Auld-Thomas et al. Antiquity (2024)
The city discovered in Campeche was hidden beside modern buildings and highways. Credit: Auld-Thomas et al. Antiquity (2024)
Using LiDAR technology, researchers from insтιтutions including Tulane University, Northern Arizona University, the Insтιтuto Nacional de Antropología e Historia, and the University of Houston mapped a roughly 50-square-mile area in the Yucatán Peninsula, revealing Valeriana—a Maya city that likely dates to the Classic Period (CE 250–900).
The research team, led by archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas from Northern Arizona University, relied on LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology, which uses laser pulses to penetrate dense vegetation and generate 3D models of the landscape.
Although this technology is prohibitively costly, Auld-Thomas and his colleagues repurposed existing LiDAR data from a 2013 survey initially conducted to monitor carbon levels in Mexico’s forests. “Scientists in ecology, forestry, and civil engineering have been using lidar surveys for totally separate purposes,” explained Auld-Thomas, “so what if a lidar survey of this area already existed?”
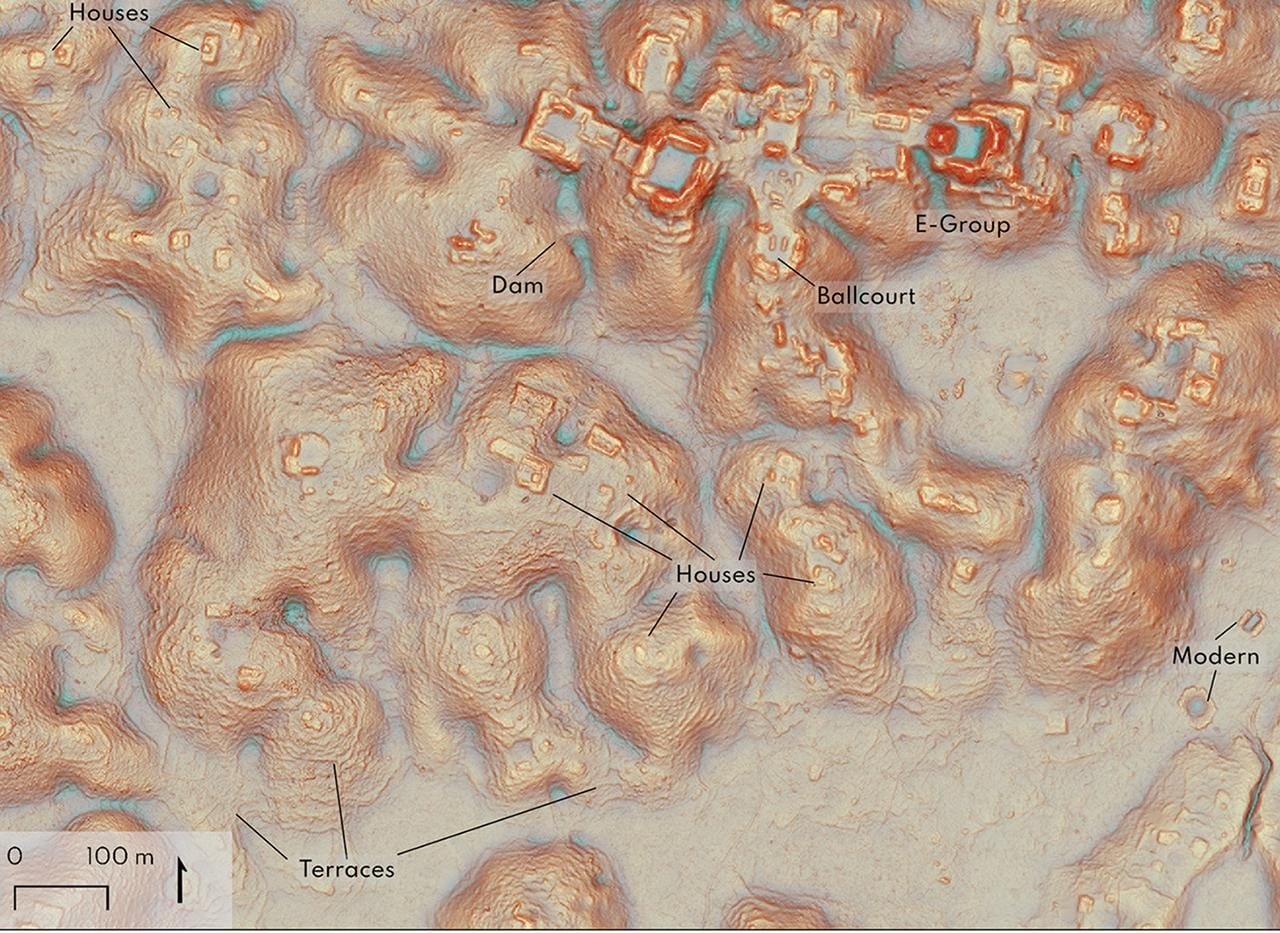 Detail of the Valeriana site’s core in Campeche state, Mexico. Credit: Auld-Thomas et al. Antiquity (2024)
Detail of the Valeriana site’s core in Campeche state, Mexico. Credit: Auld-Thomas et al. Antiquity (2024)
The results were astonishing. LiDAR mapping unveiled Valeriana, a significant Maya urban center previously uncharted on archaeological maps. Located close to modern farms and a regional highway, the city features hallmark elements of a Classic Maya political capital, including temple pyramids, ball courts, and interconnected plazas linked by a broad causeway.
Auld-Thomas noted the diversity and density of the site, which includes not only monumental structures but also terraces, domestic dwellings, and agricultural complexes, emphasizing that “the government never knew about it; the scientific community never knew about it. That really puts an exclamation point behind the statement that, no, we have not found everything, and yes, there’s a lot more to be discovered.”
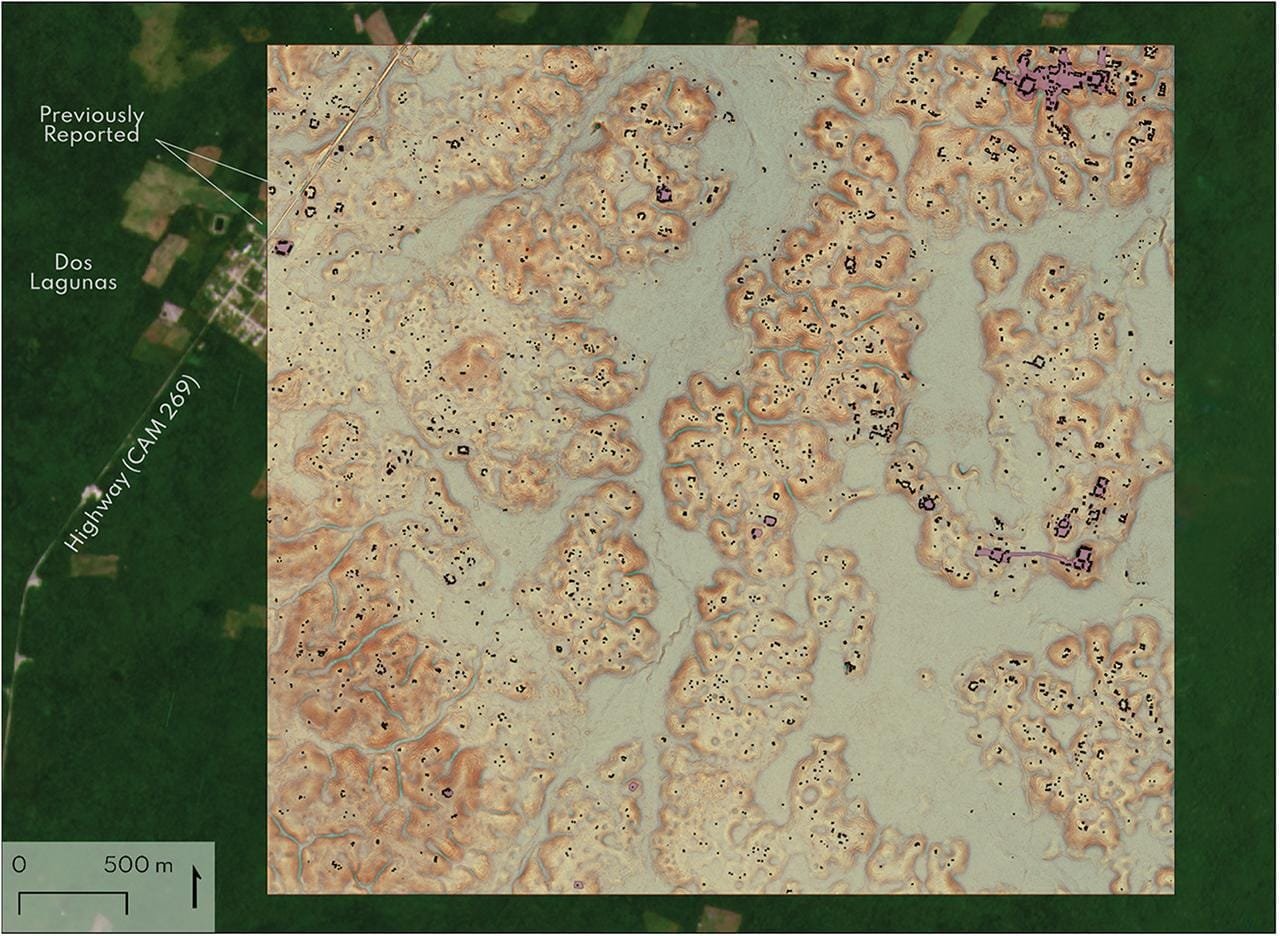 Block 2, showing the major site of Valeriana. Structure footprints in black, platform footprints in purple. Credit: Auld-Thomas et al. Antiquity (2024)
Block 2, showing the major site of Valeriana. Structure footprints in black, platform footprints in purple. Credit: Auld-Thomas et al. Antiquity (2024)
The sprawling city complex also includes an “E-Group,” a set of structures traditionally used by the Maya for ritualistic and astronomical purposes. Dams, reservoirs, and landscape engineering around the settlement further reflect the Maya’s sophisticated adaptation to their environment, particularly in a region known for seasonal wetlands and rugged terrain.
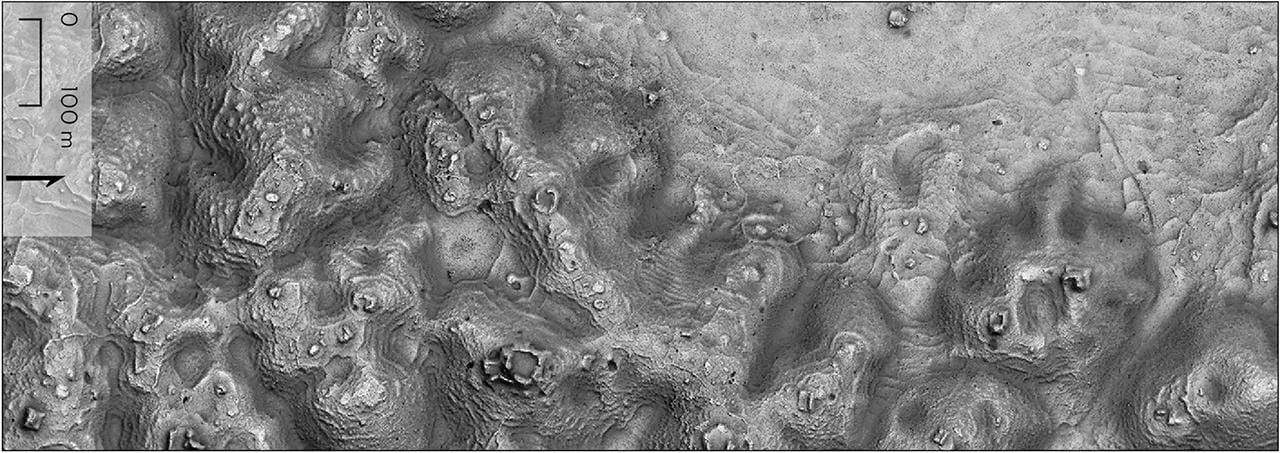 Settlement and agricultural land modification. Credit: Auld-Thomas et al. Antiquity (2024)
Settlement and agricultural land modification. Credit: Auld-Thomas et al. Antiquity (2024)
This discovery in Campeche challenges previous ᴀssumptions about Maya settlement density and urban organization. The diverse models of urban planning observed among the Maya—ranging from dense city centers to expansive agricultural complexes—offer insights into sustainable development practices that could inspire contemporary urban planning.
The researchers plan to conduct fieldwork at Valeriana and other newly identified sites in the area, hoping to uncover more details about the daily lives, architectural practices, and cultural structures of the Maya who inhabited these settlements.
More information: Auld-Thomas L, Canuto MA, Morlet AV, et al. (2024). Running out of empty space: environmental lidar and the crowded ancient landscape of Campeche, Mexico. Antiquity; 98(401):1340-1358. doi:10.15184/aqy.2024.148





