Researchers have uncovered the first physical evidence of hallucinogenic substances in an ancient Egyptian vase, shedding light on mysterious rituals from over 2,000 years ago. The investigation, led by Professor Davide Tanasi of the University of South Florida, focused on a Bes mug housed at the Tampa Museum of Art, which depicts Bes, the ancient Egyptian deity ᴀssociated with childbirth, protection, and magical purification. The study, published in Scientific Reports, combines cutting-edge chemical, genetic, and spectroscopic analyses to reveal the ingredients of a psycH๏τropic concoction likely used in magical rituals.
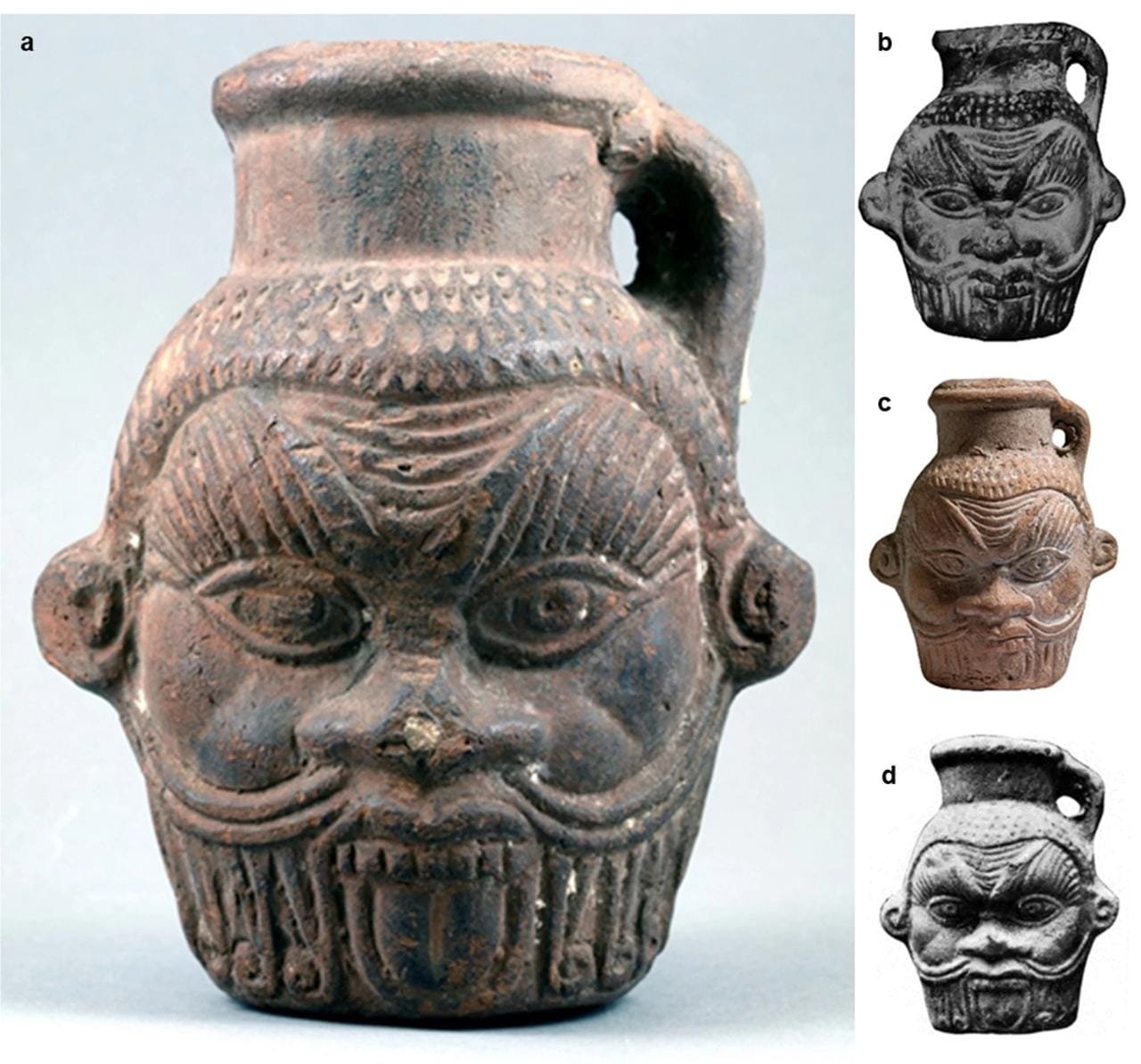 Drinking vessel in the shape of Bes head; El-Fayūm Oasis, Egypt; Ptolemaic-Roman period (4th century BCE − 3rd century CE), (courtesy of the Tampa Museum of Art, Florida). Credit: D. Tanasi et al. Scientific Reports (2024)
Drinking vessel in the shape of Bes head; El-Fayūm Oasis, Egypt; Ptolemaic-Roman period (4th century BCE − 3rd century CE), (courtesy of the Tampa Museum of Art, Florida). Credit: D. Tanasi et al. Scientific Reports (2024)
The Bes mug was donated to the museum in 1984. Decorated with the face of Bes, the vase’s design connects it to fertility and protective practices. However, its exact use had remained speculative, with theories ranging from holding sacred water to being part of magic rituals.
“For a very long time now, Egyptologists have been speculating what mugs with the head of Bes could have been used for,” said Branko van Oppen, curator of Greek and Roman art at the Tampa Museum of Art and co-author of the study. “This research teaches us about magic rituals in the Greco-Roman period in Egypt.”
Using innovative techniques, including metabolomics and synchrotron radiation-based Fourier Transformed Infrared microSpectroscopy (SR µ-FTIR), the team identified a complex mixture of ingredients. The concoction included plants with psycH๏τropic and medicinal properties such as Peganum harmala (wild rue), Egyptian blue lotus (Nymphaea nouchali var. caerulea), and a plant from the Cleome genus. Additionally, honey, sesame seeds, pine nuts, licorice, and grapes were used to flavor and color the liquid, making it resemble blood. The presence of fermented fruit-based liquids, proteins, and metabolites added further complexity to the brew.
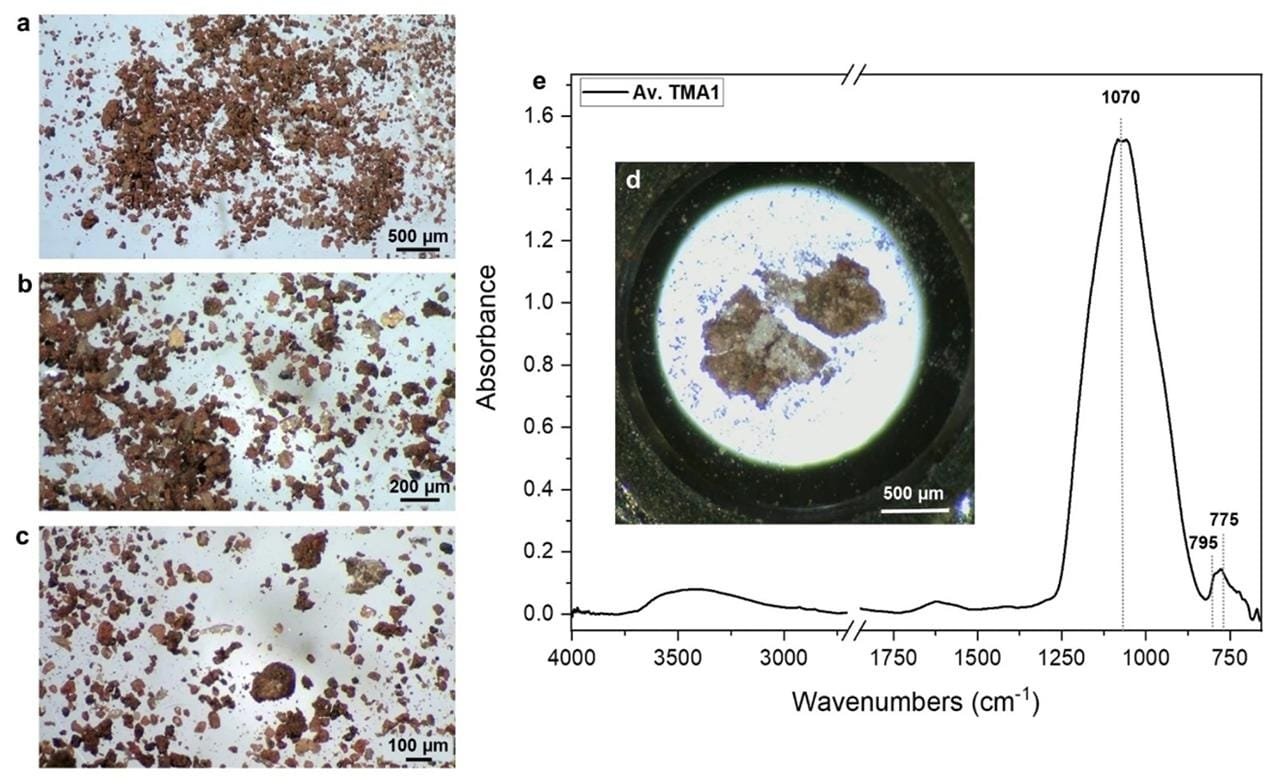 (a–c) optical image of the sample collected from the Bes vessel at different magnifications. (d) optical image of sample TMA1 flattened on half diamond compression cell. (e) average spectrum of sample TMA1. Credit: D. Tanasi et al. Scientific Reports (2024)
(a–c) optical image of the sample collected from the Bes vessel at different magnifications. (d) optical image of sample TMA1 flattened on half diamond compression cell. (e) average spectrum of sample TMA1. Credit: D. Tanasi et al. Scientific Reports (2024)
The analysis also detected traces of human bodily fluids, such as blood and saliva, suggesting their intentional inclusion in the mixture. According to the researchers, these findings indicate that the vase’s contents were likely consumed as part of a ritual aimed at inducing hallucinations or prophetic dreams.
The study draws connections between the Bes mug’s usage and the “Myth of the Solar Eye,” where Bes calms Hathor, a sky goddess, with a drug-laced alcoholic beverage disguised as blood. This act lulls Hathor into a deep sleep, symbolizing a resolution of conflict. Scholars suggest that rituals involving Bes mugs may have reenacted this myth, combining psychoactive substances and storytelling to deepen spiritual experiences.
Another significant context for the rituals was fertility and childbirth. The Bes Chambers at Saqqara, near the Great Pyramids of Giza, are believed to have been sites where women sought divine ᴀssistance during pregnancies, a period fraught with risks in the ancient world. “This combination of ingredients may have been used in a dream-vision inducing magic ritual within the context of this dangerous period of childbirth,” Van Oppen explained. Such rituals could also include oracular practices, where participants sought prophetic dreams about their futures or pregnancies.
The research, part of the Mediterranean Diet Archaeology project, involved collaborations with scientists from the University of Trieste and the University of Milan.
University of South Florida
More information: Tanasi, D., van Oppen de Ruiter, B.F., Florian, F. et al. (2024). Multianalytical investigation reveals psycH๏τropic substances in a ptolemaic Egyptian vase. Sci Rep 14, 27891. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-78721-8





