Researchers have uncovered the first direct evidence that the Clovis people, a prehistoric group who lived in North America around 13,000 years ago, primarily relied on mammoths and other large animals as their main food source.
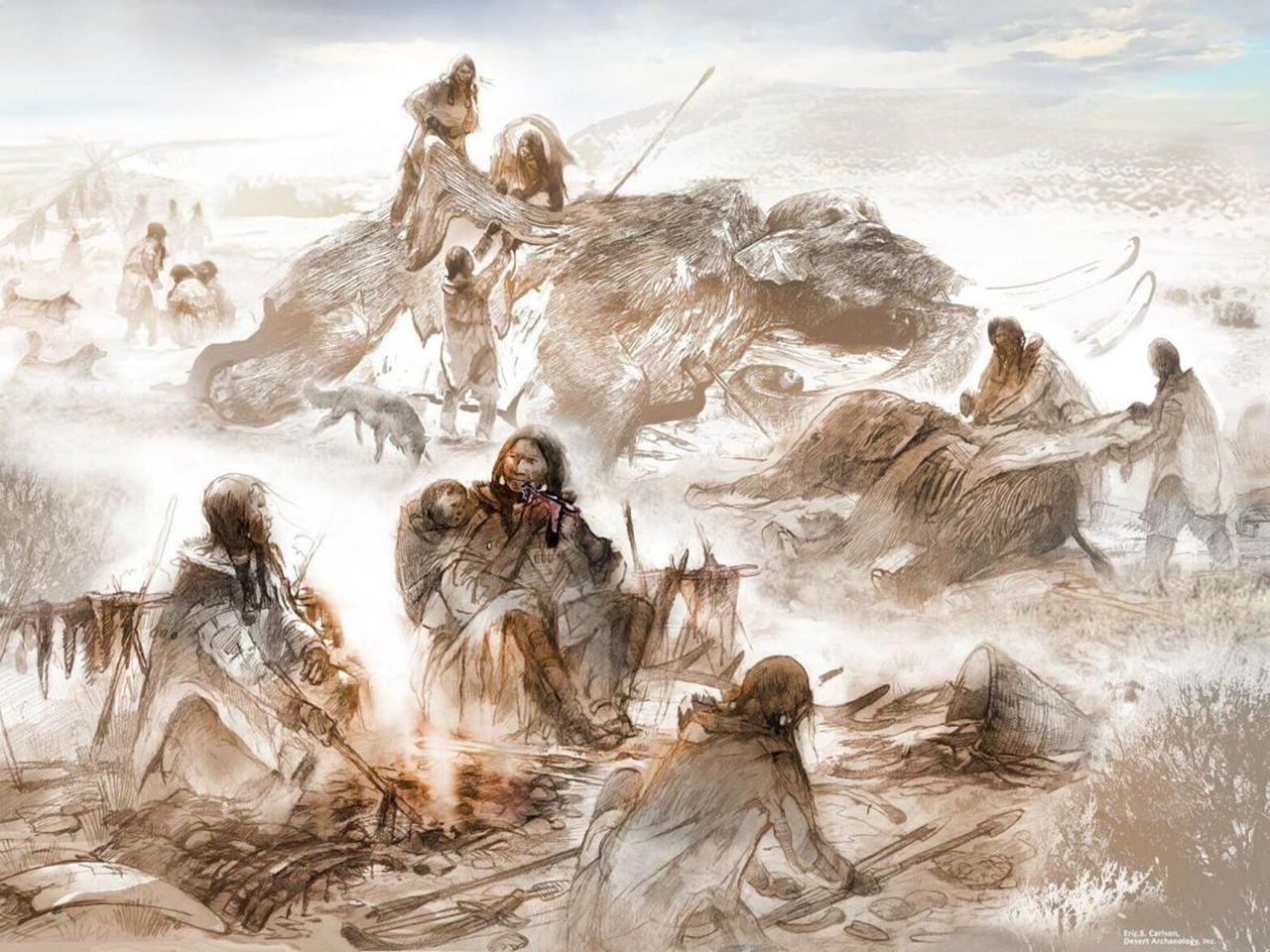 This artistic reconstruction of Clovis family life from approximately 13,000 years ago portrays the infant Anzick-1 and his mother consuming mammoth meat beside a hearth. Credit: The image was created in a collaboration between the artist, Eric Carlson (Desert Archaeology, Inc.) and archaeologists Ben Potter (University of Alaska Fairbanks) and Jim Chatters (McMaster University)
This artistic reconstruction of Clovis family life from approximately 13,000 years ago portrays the infant Anzick-1 and his mother consuming mammoth meat beside a hearth. Credit: The image was created in a collaboration between the artist, Eric Carlson (Desert Archaeology, Inc.) and archaeologists Ben Potter (University of Alaska Fairbanks) and Jim Chatters (McMaster University)
A study, published in Science Advances on December 4, used advanced isotopic analysis to reveal that these ancient humans relied heavily on mammoths and other large animals for sustenance.
Evidence from Isotopic Fingerprinting
The findings are based on chemical analyses of the remains of Anzick-1, an 18-month-old child discovered at a Clovis burial site in Montana. Since the child was still nursing, researchers examined the isotopic fingerprint in his bones to infer his mother’s diet.
“Isotopes provide a chemical fingerprint of a consumer’s diet and can be compared with those from potential diet items to estimate the proportional contribution of different diet items,” explained Mat Wooller, a study co-author and director of the Alaska Stable Isotope Facility at the University of Alaska Fairbanks.
The analysis revealed that approximately 40% of the mother’s diet consisted of mammoth meat. Other large animals, such as elk and bison, made up most of the remaining portion, while smaller mammals and plants played a minimal role. Remarkably, her diet closely resembled that of the now-extinct scimitar cat, a predator specializing in mammoth hunting.
 Clovis Hunting Strategies
Clovis Hunting Strategies
The study supports the hypothesis that Clovis people were highly specialized hunters of megafauna. “What’s striking to me is that this confirms a lot of data from other sites,” said Ben Potter, co-lead author and archaeologist at the University of Alaska Fairbanks. “For example, the animal parts left at Clovis sites are dominated by megafauna, and the projectile points are large, affixed to darts, which were efficient distance weapons.”
Related: Mammoths and early human society
Mammoths, which migrated across vast distances in northern Asia and the Americas, provided a reliable and energy-rich resource. This dependence on large animals likely contributed to the Clovis people’s rapid spread across North and South America within just a few centuries. “The focus on mammoths helps explain how Clovis people could spread throughout North America and into South America in just a few hundred years,” noted James Chatters, co-lead author and archaeologist at McMaster University.
Human Expansion and Megafauna Extinction
The research also adds to the debate over the role humans played in the extinction of Ice Age megafauna. The arrival of humans in the Americas coincided with significant environmental changes that reduced suitable habitats for large animals. This dual pressure from climate change and skilled hunters may have hastened their decline.
 Location of Anzick site, faunal samples (circles) used in this study, and major Clovis sites (triangles). Credit: Chatters et al., Sci. Adv. (2024)
Location of Anzick site, faunal samples (circles) used in this study, and major Clovis sites (triangles). Credit: Chatters et al., Sci. Adv. (2024)
“If the climate is changing in a way that reduces the suitable habitat for some of these megafauna, then it makes them potentially more susceptible to human predation. These people were very effective hunters,” said Potter. Chatters added, “You had the combination of a highly sophisticated hunting culture—with skills honed over 10,000 years in Eurasia—meeting naïve populations of megafauna under environmental stress.”
Collaboration with Indigenous Communities
An essential component of the study was its outreach to Native American communities in Montana, Wyoming, and Idaho. Shane Doyle, executive director of Yellowstone Peoples, facilitated discussions with tribal representatives. He praised the research team for their inclusive approach, saying, “This study reshapes our understanding of how Indigenous people across America thrived by hunting one of the most dangerous and dominant animals of the day, the mammoth.”
This research represents the first direct evidence of the Clovis people’s reliance on mammoths and other large animals for food.
More information: Chatters, J. C., Potter, B. A., Fiedel, S. J., Morrow, J. E., Jᴀss, C. N., & Wooller, M. J. (2024). Mammoth featured heavily in Western Clovis diet. Science Advances, 10(49). doi:10.1126/sciadv.adr3814





