A study led by researchers at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) has unveiled the oldest known bowstrings in Europe. Artifacts discovered in the Cueva de Los Murciélagos (Cave of the Bats) in Albuñol, Granada, date back approximately 7,000 years (5300–4900 BCE) and reveal sophisticated techniques and materials that redefine our understanding of prehistoric weaponry.
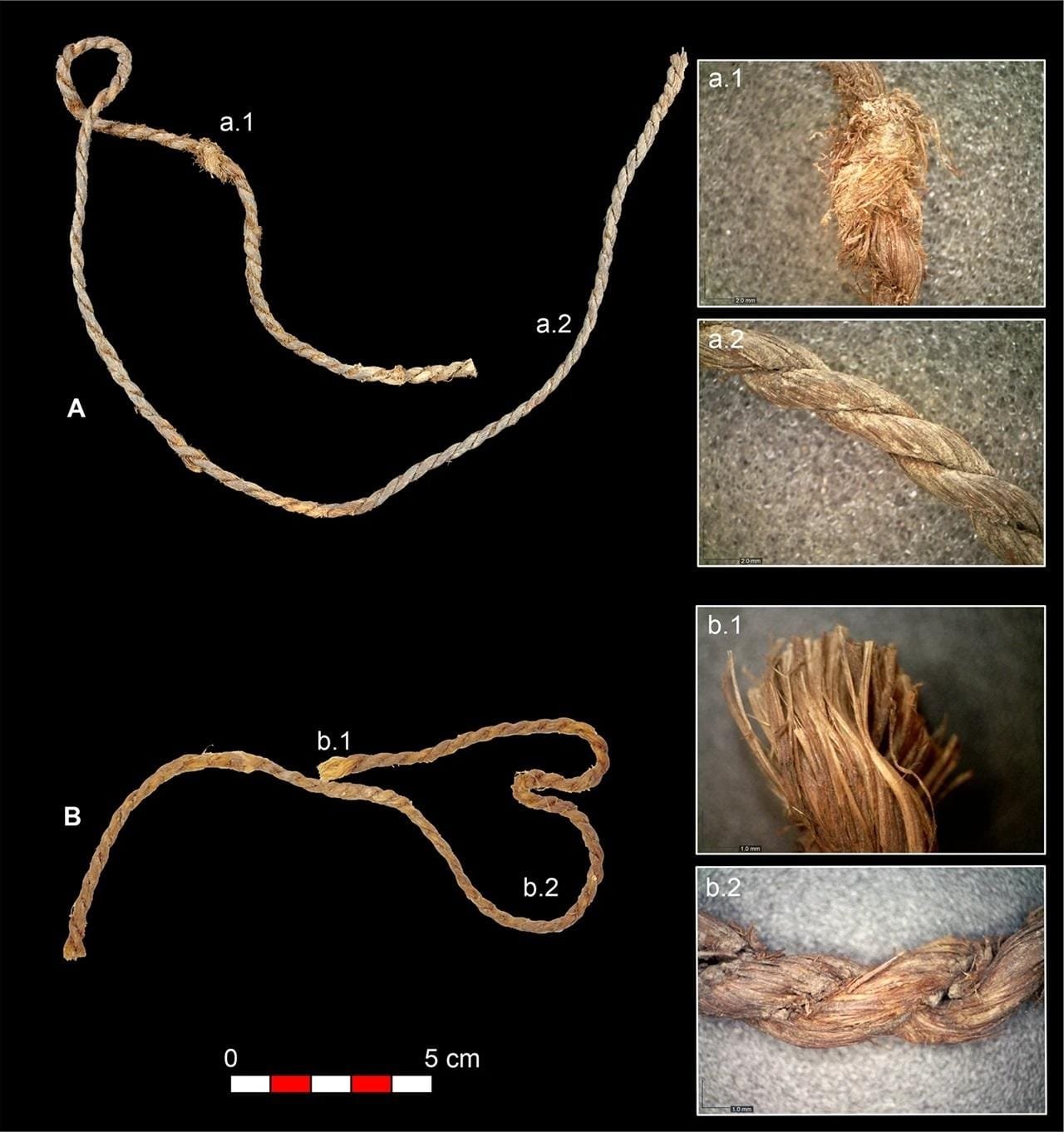 Cordage fragments from Cueva de los Murciélagos identified as possible bowstrings. Credit: I. Bertin et al., Scientific Reports (2024)
Cordage fragments from Cueva de los Murciélagos identified as possible bowstrings. Credit: I. Bertin et al., Scientific Reports (2024)
The arid conditions of the Cueva de Los Murciélagos preserved these artifacts in remarkable condition. Among the findings are bowstrings crafted from the tendons of various animals, including goats, boar, and roe deer. These tendons were intricately twisted to create ropes that combined strength and flexibility, meeting the demands of skilled Neolithic archers. “This degree of precision and technical mastery, where every detail counts, attests to the exceptional knowledge of these Neolithic artisans,” stated Raquel Piqué, a co-author of the study and archaeologist at UAB.
Arrow shafts were constructed from a combination of olive wood, willow wood, and reeds, materials carefully chosen to enhance their ballistic properties. According to UAB researcher Ingrid Bertin, olive wood’s strength and density contributed to stability and penetration, while willow’s lighter weight facilitated speed and distance. Reeds were used for the back portions of some arrows, marking the first confirmed use of this material in prehistoric Europe.
The arrows were coated with birch tar, a substance created through controlled heating of birch bark. Beyond its protective qualities, birch tar may have added aesthetic appeal, reflecting the Neolithic artisans’ attention to both functionality and design.
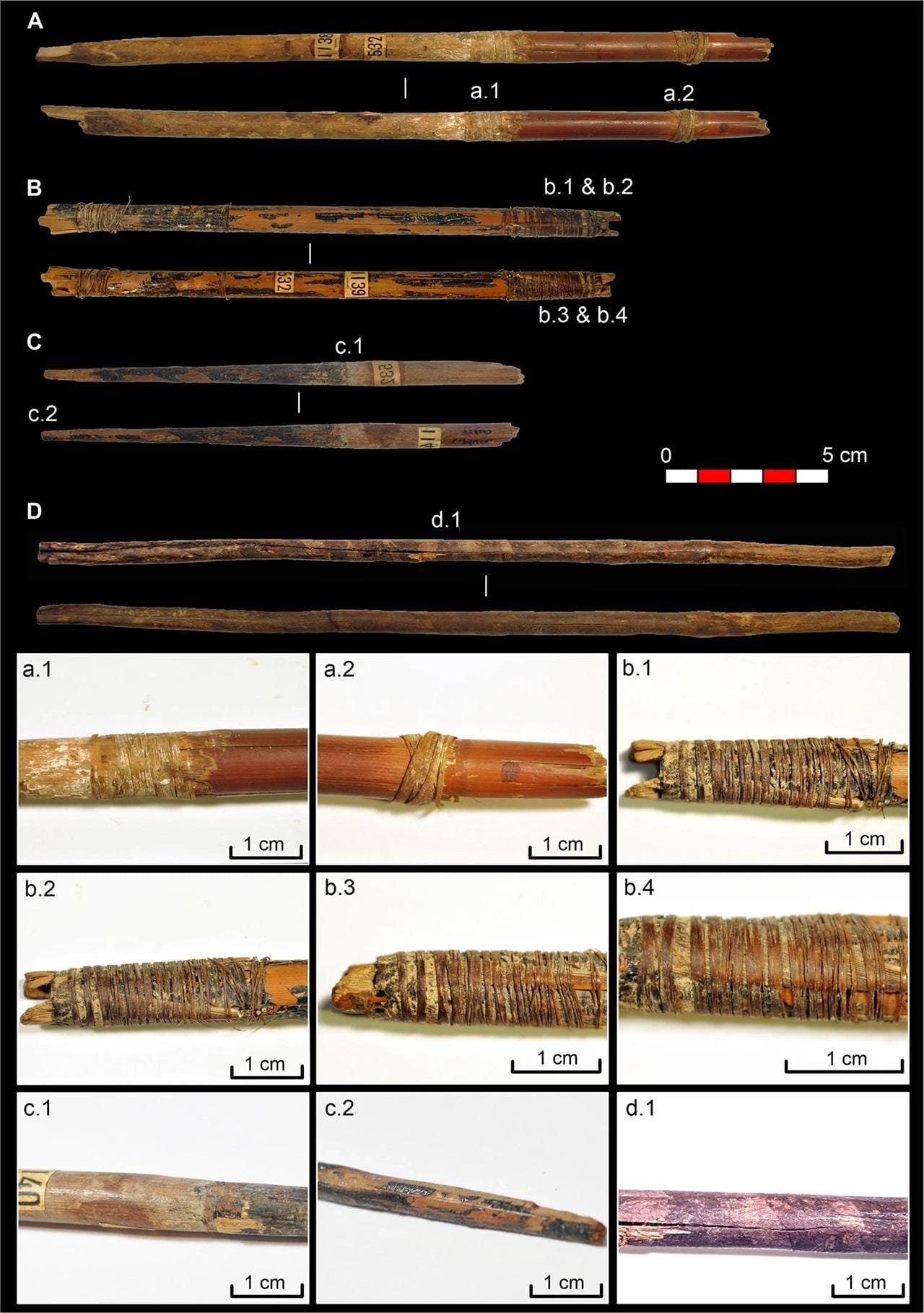 Plant-based arrowheads and shafts from Cueva de los Murciélagos. Credit: I. Bertin et al., Scientific Reports (2024)
Plant-based arrowheads and shafts from Cueva de los Murciélagos. Credit: I. Bertin et al., Scientific Reports (2024)
The placement of these advanced weapons in a funerary context suggests that archery held a significant symbolic or spiritual role in Neolithic societies. Researchers speculate that these tools might have been used in rituals or buried as grave goods, pointing to their importance beyond practical hunting or combat uses.
The findings are part of the MUTERMUR project and funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 program. The team employed advanced microscopy and biomolecular analyses to identify proteins, lipids, and other organic materials in the artifacts. This interdisciplinary approach revealed the high level of craftsmanship and local resource utilization that characterized Neolithic life in the region.
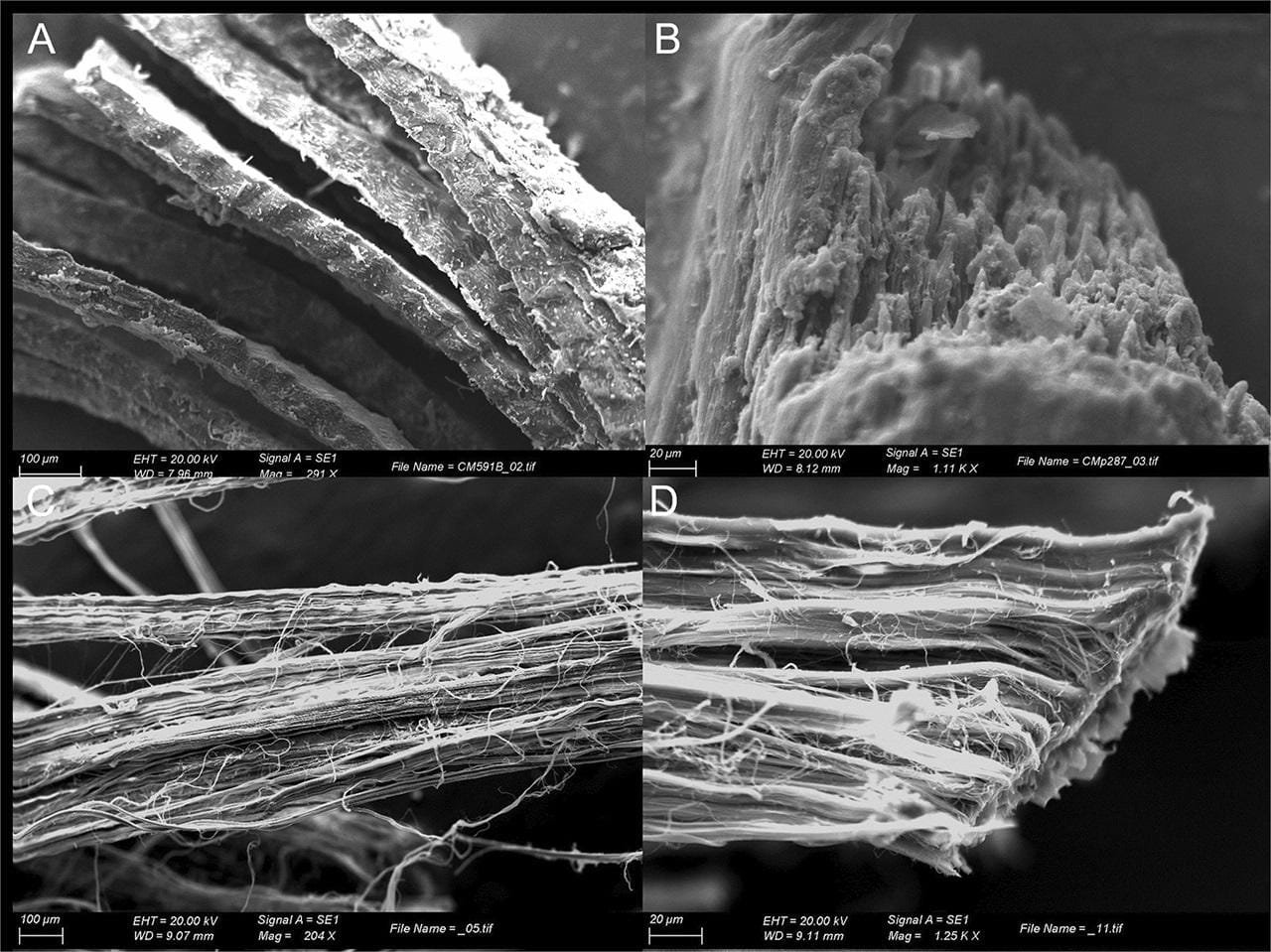 SEM micropH๏τographs of the cords (a) CM-591b: structure of fibres with an undulated aspect, (b) CM-P287: detail of the collagen fibres, (c and d) modern sinew. Credit: I. Bertin et al., Scientific Reports (2024)
SEM micropH๏τographs of the cords (a) CM-591b: structure of fibres with an undulated aspect, (b) CM-P287: detail of the collagen fibres, (c and d) modern sinew. Credit: I. Bertin et al., Scientific Reports (2024)
The study’s authors highlight how the integration of materials such as animal tendons and olive wood demonstrates a deep understanding of natural properties. “Future experiments may clarify whether these arrows could have been used for hunting or close-range combat, or whether they could have been non-lethal arrows,” noted Bertin.
The findings underscore the innovative spirit of Neolithic societies, whose mastery of materials and technology laid the groundwork for advancements in weaponry and tools across Europe.
The study is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
More information: Bertin, I., Martín-Seijo, M., Martínez-Sevilla, F. et al. (2024). First evidence of early neolithic archery from Cueva de los Murciélagos (Albuñol, Granada) revealed through combined chemical and morphological analysis. Sci Rep 14, 29247. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-77224-w





