Archaeological excavations conducted by the State Office for Monument Preservation (LAD) within the Stuttgart Regional Council between August and October 2024 near Altenburg, Germany, have revealed significant findings at the late Celtic oppidum Altenburg-Rheinau. This settlement, which thrived during the first century BCE, was a major center for trade and specialized crafts north of the Alps.
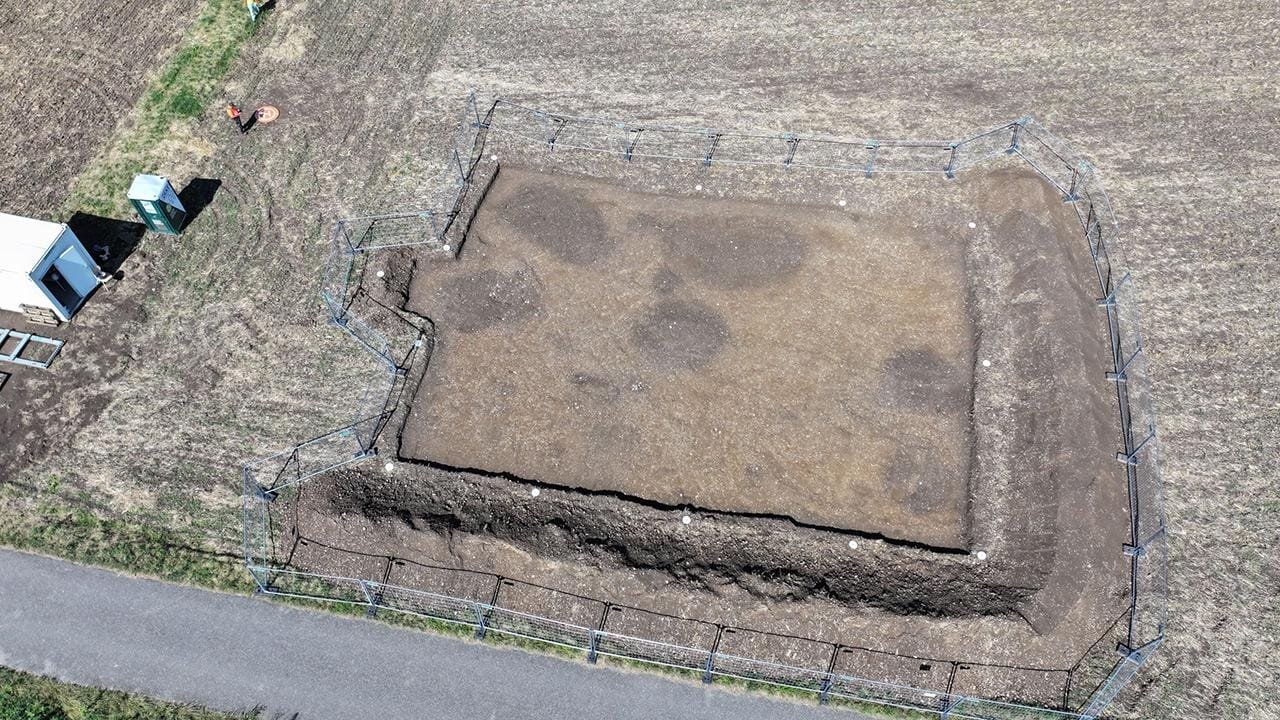 One of the excavation sites from 2024: After removing the topsoil, large storage pits are visible as discolorations. Credit: LAD/Francois Ohl
One of the excavation sites from 2024: After removing the topsoil, large storage pits are visible as discolorations. Credit: LAD/Francois Ohl
The Altenburg-Rheinau oppidum spans two peninsulas: Schwaben in Germany and Au in Switzerland, both fortified with defensive walls. Excavations on the Schwaben peninsula, initiated by the University of Tübingen in the 1970s, provided early evidence of settlement structures. Subsequent investigations by the LAD in 2022 and 2023 unearthed additional artifacts, including ceramics and coins.
The 2024 excavations focused near the fortification wall on the Schwaben peninsula. Project leader Dr. Günther Wieland, Head of the Metal Age Department at LAD, highlighted the discovery of large cylindrical pits up to 2.5 meters deep. “These pits, with distinct backfill layers, were likely used for food storage,” Wieland explained. Some pits had rectangular or oval bases and may have been accessed via earthen stairs or ramps. While evidence of aboveground residential structures remains sparse, a square post structure uncovered nearby is thought to have been a storage building.
Artifacts unearthed from the Altenburg-Rheinau site underscore its importance as a hub of trade and cultural exchange. Local coarse and fine pottery fragments were found alongside imported wine amphorae from Italy. “Wine from the Mediterranean was a coveted luxury among the Celtic elite and a cornerstone of lucrative trade,” noted Wieland.
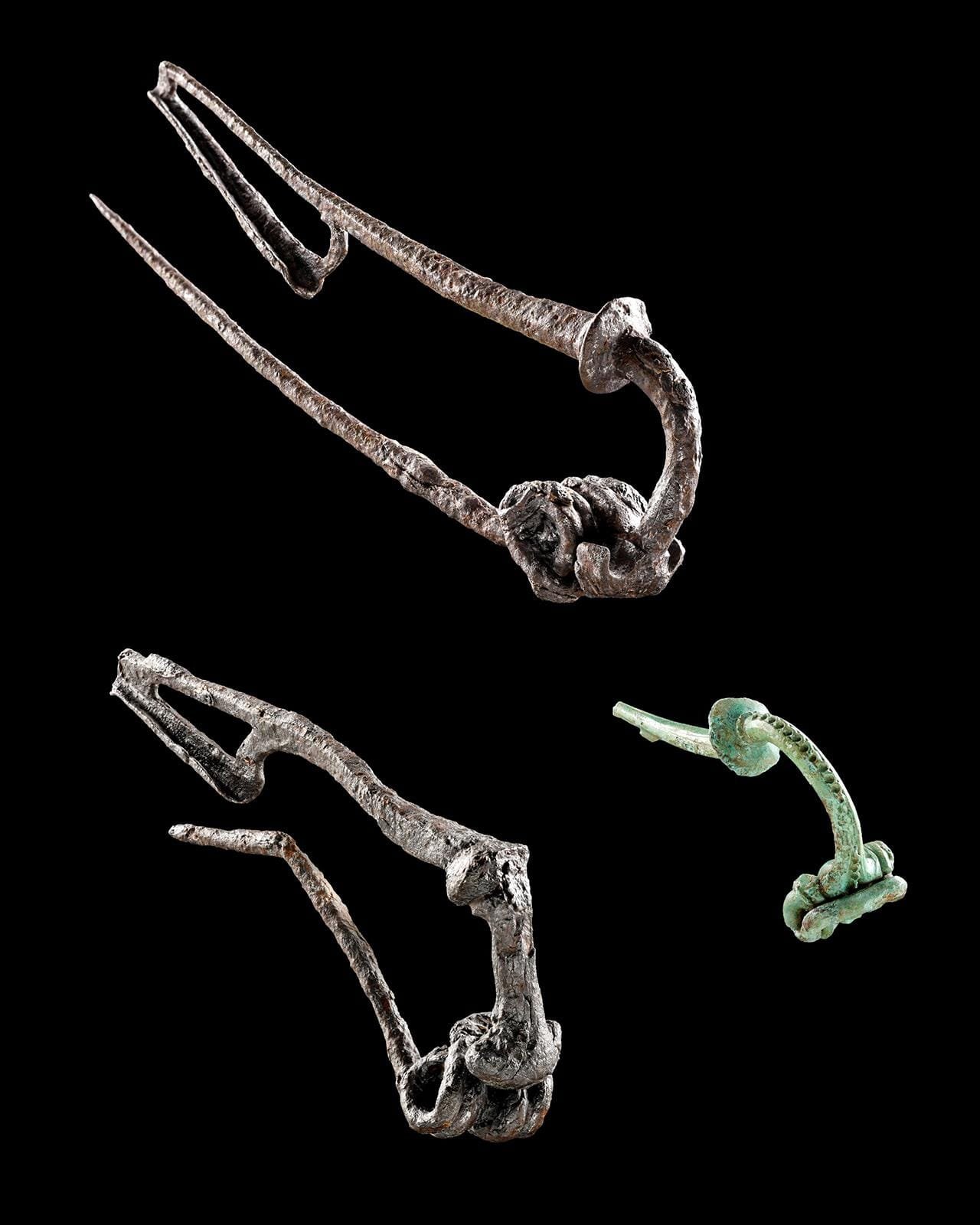 Late Celtic brooches (garment clasps) from the 1st century BC, made of bronze and iron. Credit: LAD/Yvonne Mühleis
Late Celtic brooches (garment clasps) from the 1st century BC, made of bronze and iron. Credit: LAD/Yvonne Mühleis
Coins from the first century BCE provide further evidence of a monetary economy facilitating trade. The presence of ornately decorated brooches, belt components, and other costume accessories made of bronze and iron offers a glimpse into the daily lives and craftsmanship of the Celts.
One of the most intriguing discoveries came during the 2023 excavations: a bone stylus used for writing on wax tablets. “This is rare evidence of the use of writing in the oppidum,” Wieland said. “Along with the coin economy, it was a crucial prerequisite for trade with the Mediterranean region.”
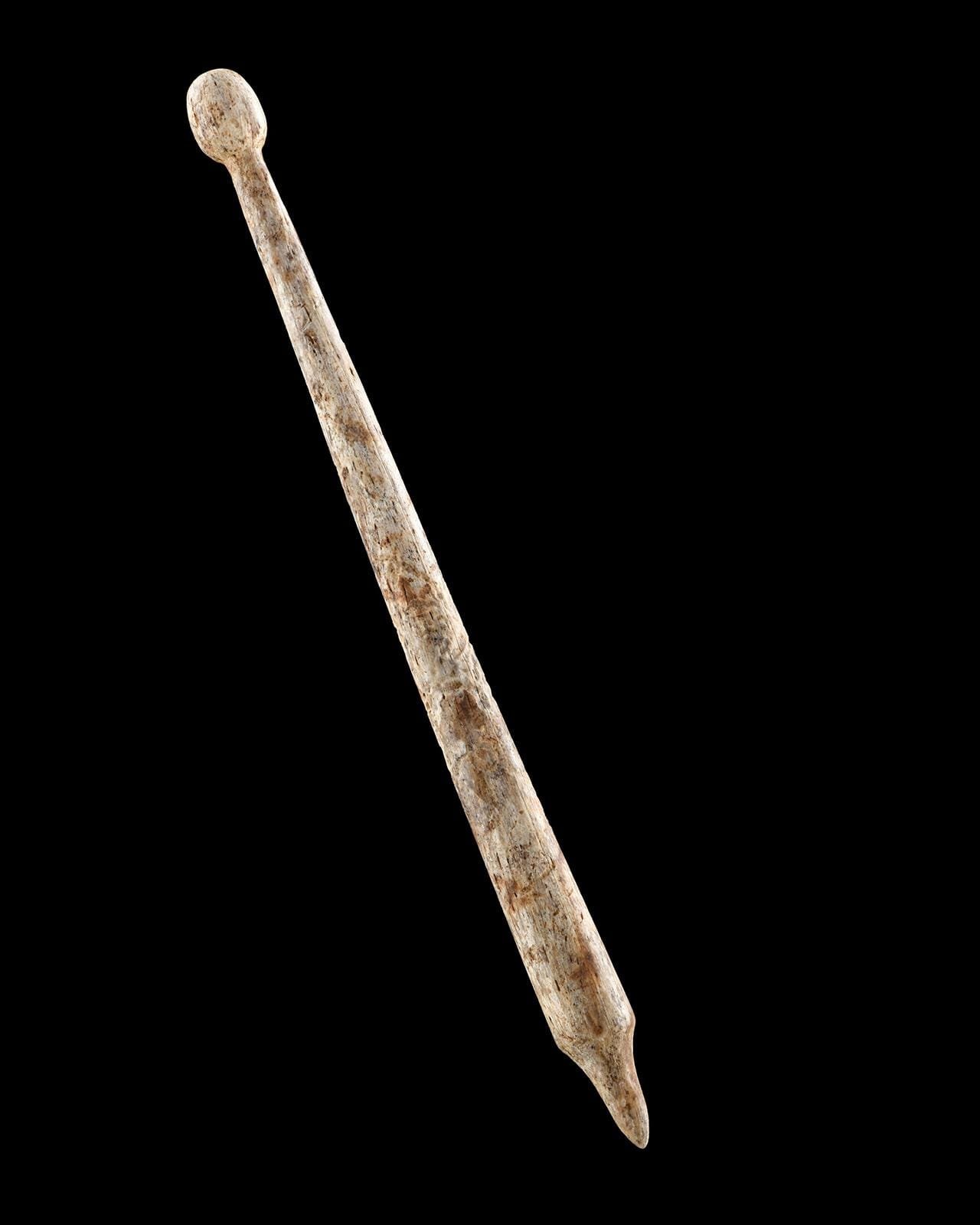 Writing implement made of bone. Credit: LAD/Yvonne Mühleis
Writing implement made of bone. Credit: LAD/Yvonne Mühleis
The large quanтιтies of well-preserved animal bones, primarily from cattle, found at the site point to organized livestock farming and specialized meat production. These findings provide a deeper understanding of the economic systems and settlement organization within the oppidum.
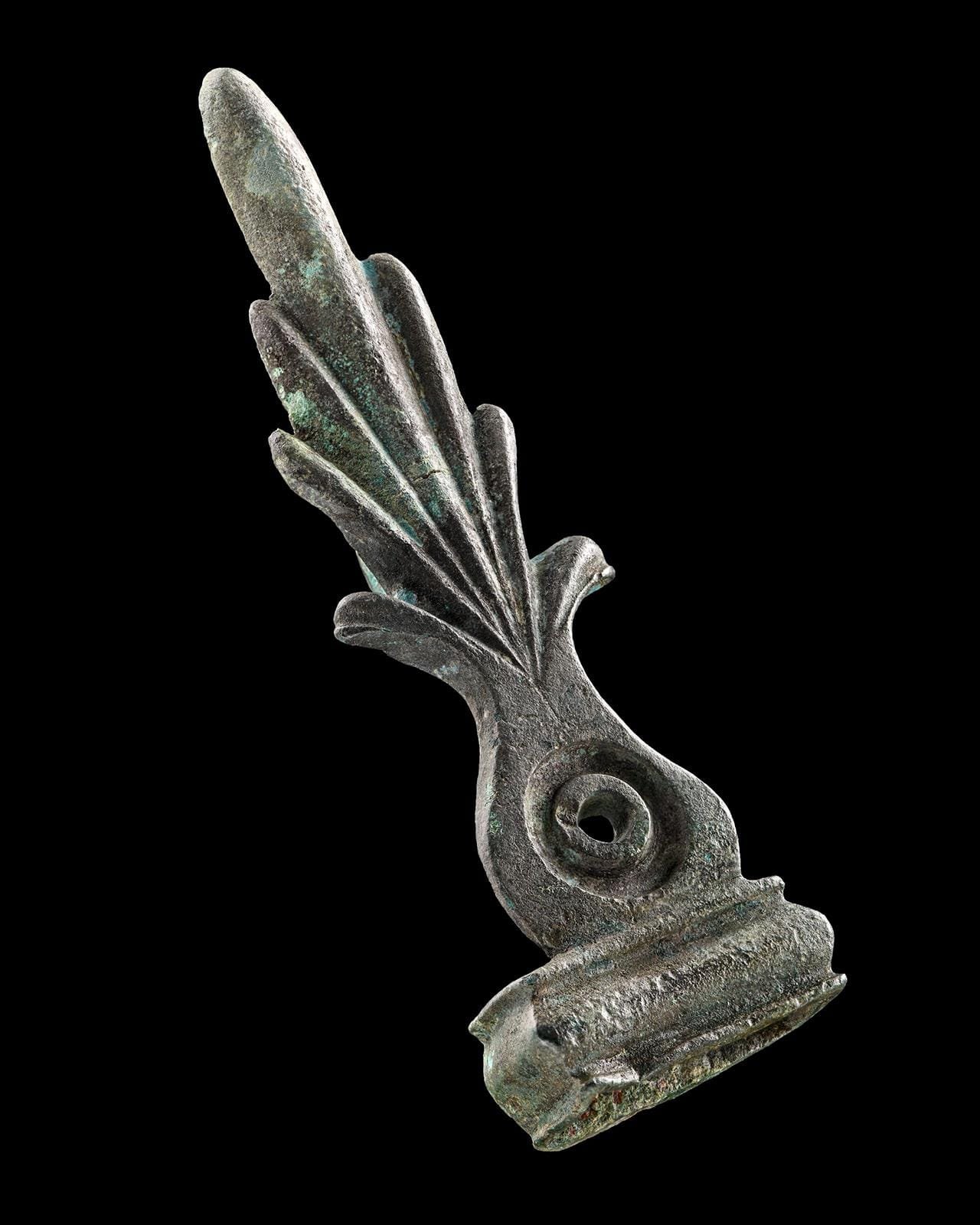 Palmette belt hook made of bronze from the 2023 excavation. Credit: LAD/Yvonne Mühleis
Palmette belt hook made of bronze from the 2023 excavation. Credit: LAD/Yvonne Mühleis
As research continues, plans are underway for further excavations in 2025.
More information: State Office for the Preservation of Monuments (LAD)





