Archaeologists have uncovered a spectacular sixth-century sword from an Anglo-Saxon cemetery near Canterbury, Kent, in a discovery hailed as one of the most remarkable of its kind. The weapon, distinguished by its exceptional preservation and craftsmanship, is being compared to the famous Sutton Hoo sword found in Suffolk in 1939.
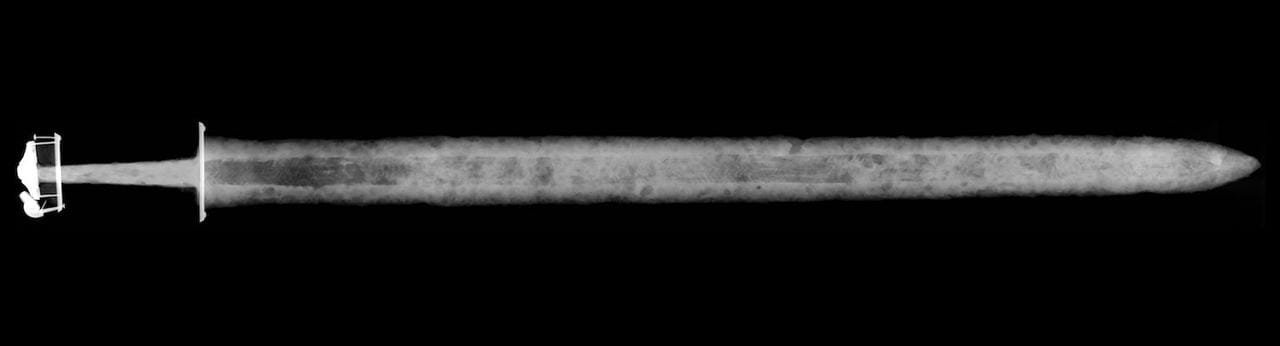 X-ray of sixth-century sword unearthed in Anglo-Saxon cemetery in the UK. Credit: Dana Goodburn-Brown
X-ray of sixth-century sword unearthed in Anglo-Saxon cemetery in the UK. Credit: Dana Goodburn-Brown
The newly unearthed sword features a silver-and-gilt hilt with intricate decorative patterns and a blade inscribed with a runic script. Even the leather-and-wood scabbard, lined with beaver fur, has survived the pᴀssage of time. A ring attached to the pommel may symbolize an oath to a king or high-ranking figure, reflecting the weapon’s elite status.
Lead archaeologist Professor Duncan Sayer of the University of Central Lancashire expressed awe at the find. “It’s really incredible, in the top echelons of swords, an elite object in every way. It rivals the swords from Dover and Sutton Hoo,” he told The Guardian. The Sutton Hoo sword, crafted with gold and cloisonné garnets, is considered a pinnacle of Anglo-Saxon craftsmanship, but this recent discovery stands out for its remarkable condition.
The cemetery, whose exact location remains undisclosed to protect the site, has so far revealed 12 graves, though researchers estimate it contains up to 200 burials. Male graves have yielded weapons such as spears and shields, while female burials include brooches, buckles, and knives. Notably, the grave containing the sword also held a gold pendant engraved with a serpent or dragon—a type of ornament typically ᴀssociated with high-status women. Archaeologists suggest it may have been an heirloom or a gift from a female relative.
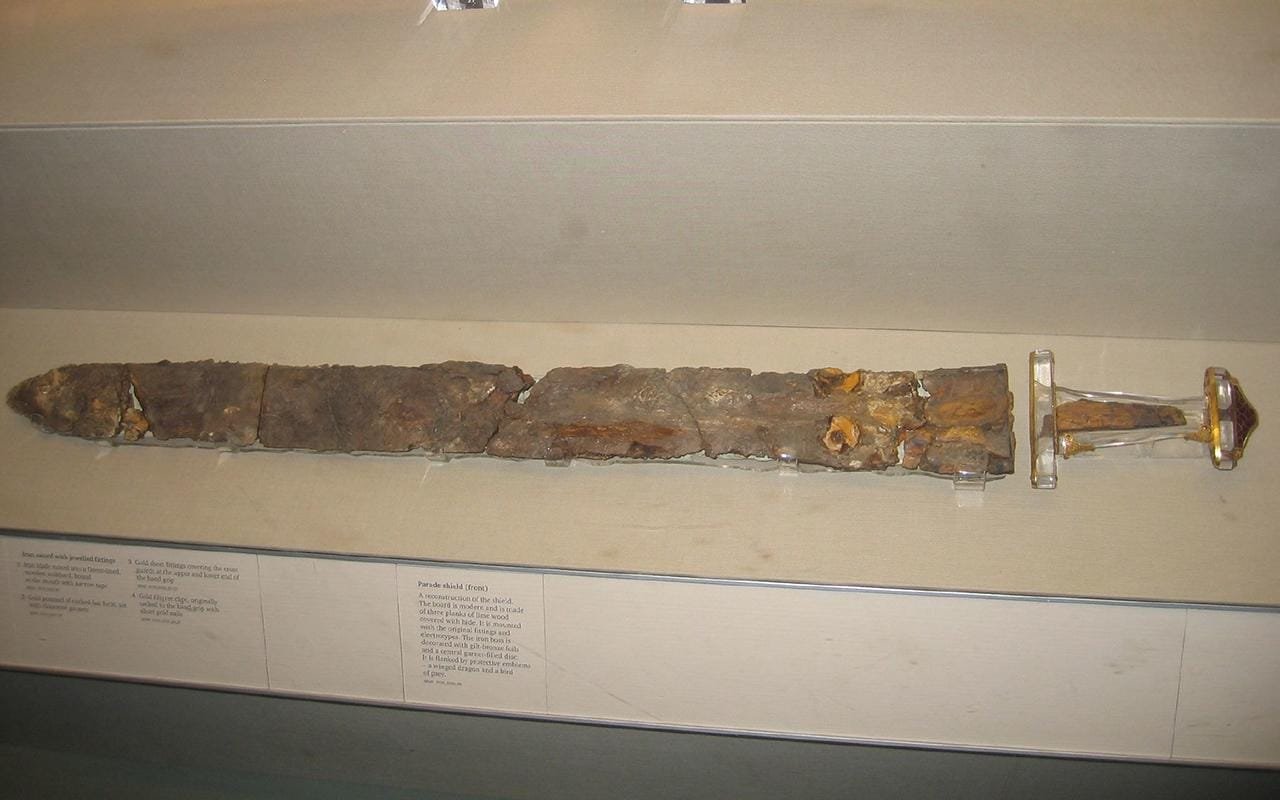 Sutton Hoo Sword. Credit: Michael Daines, Flickr
Sutton Hoo Sword. Credit: Michael Daines, Flickr
Other artifacts at the site hint at connections to regions beyond Britain. Scandinavian objects were found in a fifth-century woman’s grave, while items of Frankish origin appear in later burials. These findings illuminate the migration patterns and cultural exchanges following the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the early fifth century.
The excavation has also provided rare insights into Anglo-Saxon funerary customs. Conservator Dana Goodburn-Brown discovered fly pupae on the sword, suggesting the deceased’s body was left exposed for a time before burial, likely to allow loved ones to pay their respects. “So we’re learning something about the funerary practices,” she explained in the upcoming BBC Two series Digging for Britain.
The sword and other artifacts are undergoing conservation and will eventually be displayed at the Folkestone Museum. Prof Alice Roberts, presenter of Digging for Britain, described the site as “an extraordinary Anglo-Saxon cemetery with incredibly furnished graves… The sword is just astonishing.”





