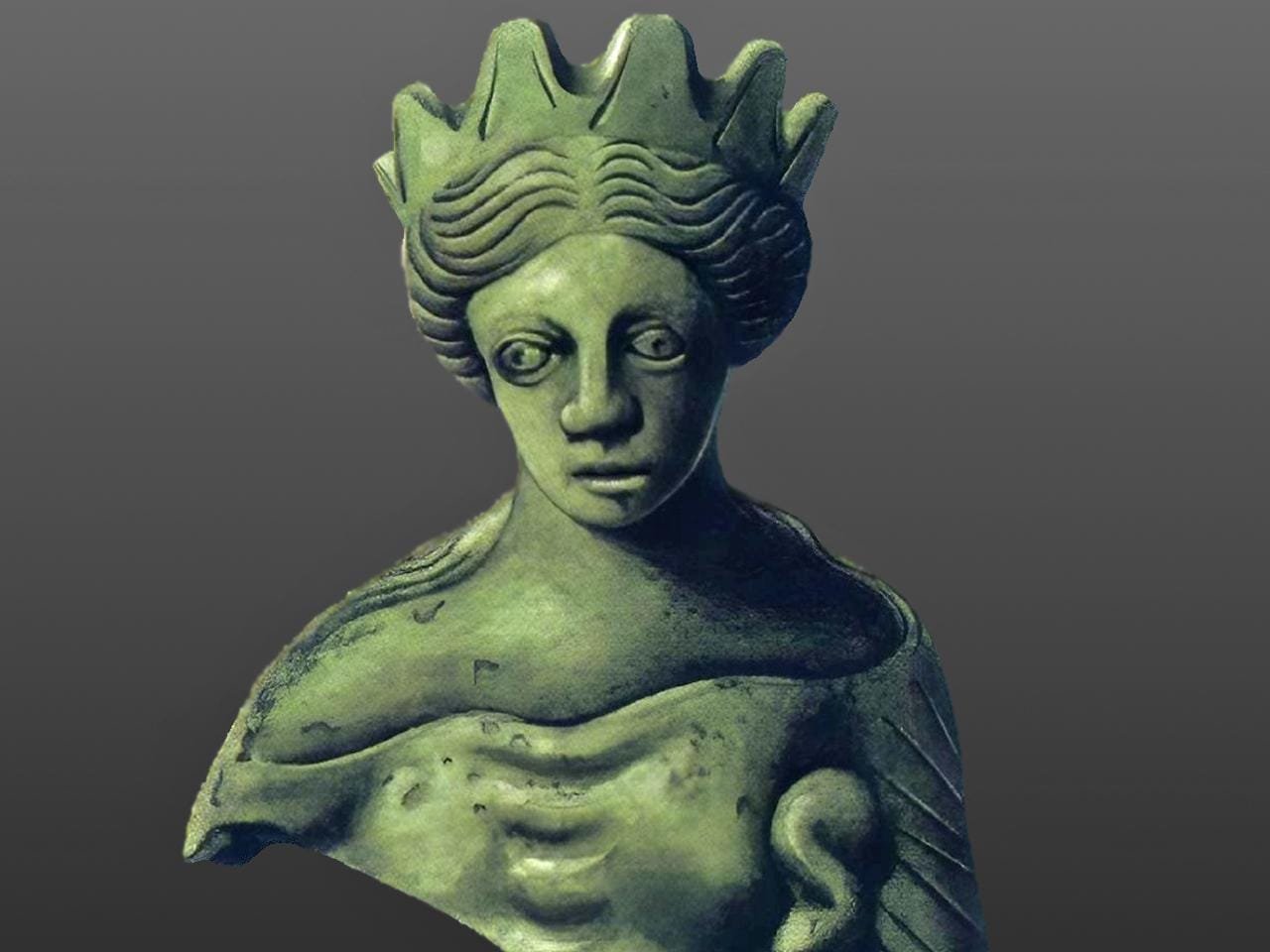
Archaeologists in northern Portugal have uncovered a unique bronze figurine dating back to the 2nd century CE in the ancient Roman city of Bracara Augusta, now modern-day Braga. The artifact, depicting a female figure with unique facial structures, has led experts in archaeology, art history, and medicine to speculate that it may provide evidence of Crouzon syndrome, a rare genetic disorder.
 2nd-century Roman bronze figurine found in Braga, Portugal. Credit: Museu de Arqueologia D. Diogo de Sousa, Manuel Santos
2nd-century Roman bronze figurine found in Braga, Portugal. Credit: Museu de Arqueologia D. Diogo de Sousa, Manuel Santos
The figurine was found atop Mount Cividade during excavations and displays physical abnormalities, including exophthalmos (protruding eyes), exotropia (misaligned eyes), and facial asymmetry. Researchers used iconodiagnosis—a technique that interprets medical conditions represented in art—to identify signs consistent with craniofacial dysostosis, or Crouzon syndrome. This genetic disorder, first described by French neurologist Octave Crouzon in 1912, causes premature fusion of skull bones, leading to distinct cranial and facial deformities.
Dr. Rui Morais, an archaeologist who analyzed the artifact, described its intricate details: “The head is adorned with a diadem of seven stylized towers, perhaps symbolizing the gates of the Roman city. The facial features—large, prominent eyes, asymmetrical lips, and a slightly tilted oval face—are rendered with remarkable precision.” The figurine’s mural crown, commonly seen on statues of city patron goddesses like Tyche and Fortuna, underscores its symbolic significance.
However, the artifact diverges from conventional representations of Greco-Roman deities. Instead of the cornucopia of abundance commonly held by such figures, the figurine wields a serpent entwined around a rod, an attribute linked to health deities such as Asclepius and Hygieia. This has led scholars to speculate that the figure represents a priestess involved in health-related rituals or perhaps a deity like Salus, the Roman counterpart of Hygieia.
 The figurine was found atop Mount Cividade during excavations and displays physical abnormalities. Credit: Museu de Arqueologia D. Diogo de Sousa, Manuel Santos
The figurine was found atop Mount Cividade during excavations and displays physical abnormalities. Credit: Museu de Arqueologia D. Diogo de Sousa, Manuel Santos
The sorrowful expression of the figurine, coupled with its unusual features, prompts questions about how ancient societies and religions treated individuals with physical differences. Some scholars suggest that these distinctive traits might have been seen as divine signs, echoing shamanic beliefs that regarded deformities as spiritual gifts.
Joseph Warkany, a pioneer in the study of congenital malformations, emphasized the value of artistic depictions in understanding historical perceptions of medical conditions: “Art provides an invaluable lens to explore human responses to medical conditions before scientific explanations existed.”
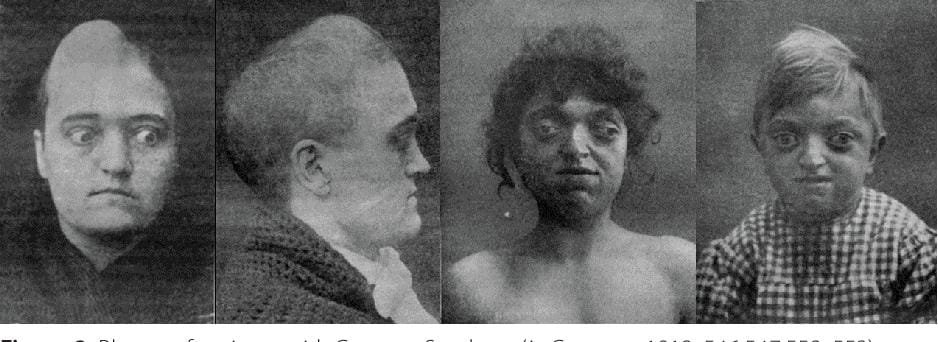 PH๏τos of patients with Crouzon Syndrom. Credit: Crouzon, 1912/Barroso, M. do S., Antropologia Portuguesa (2024)
PH๏τos of patients with Crouzon Syndrom. Credit: Crouzon, 1912/Barroso, M. do S., Antropologia Portuguesa (2024)
Although Crouzon syndrome is now well understood, this bronze statuette represents the first proposed case of the condition depicted in Greco-Roman art. Its discovery enriches our understanding of how medical anomalies were perceived within the fabric of ancient Roman society.
More information: Barroso, M. do S. (2024). A possible case of Crouzon syndrome in a female figurine from Bracara Augusta from the 2nd century CE. Antropologia Portuguesa, (41), 31–42. doi:10.14195/2182-7982_41_2





