Mysterious earth rings emerge from the hills onto the outskirts of Melbourne, Australia, in the suburb of Sunbury; they bear the secrets of hundreds of years in their silent rings.
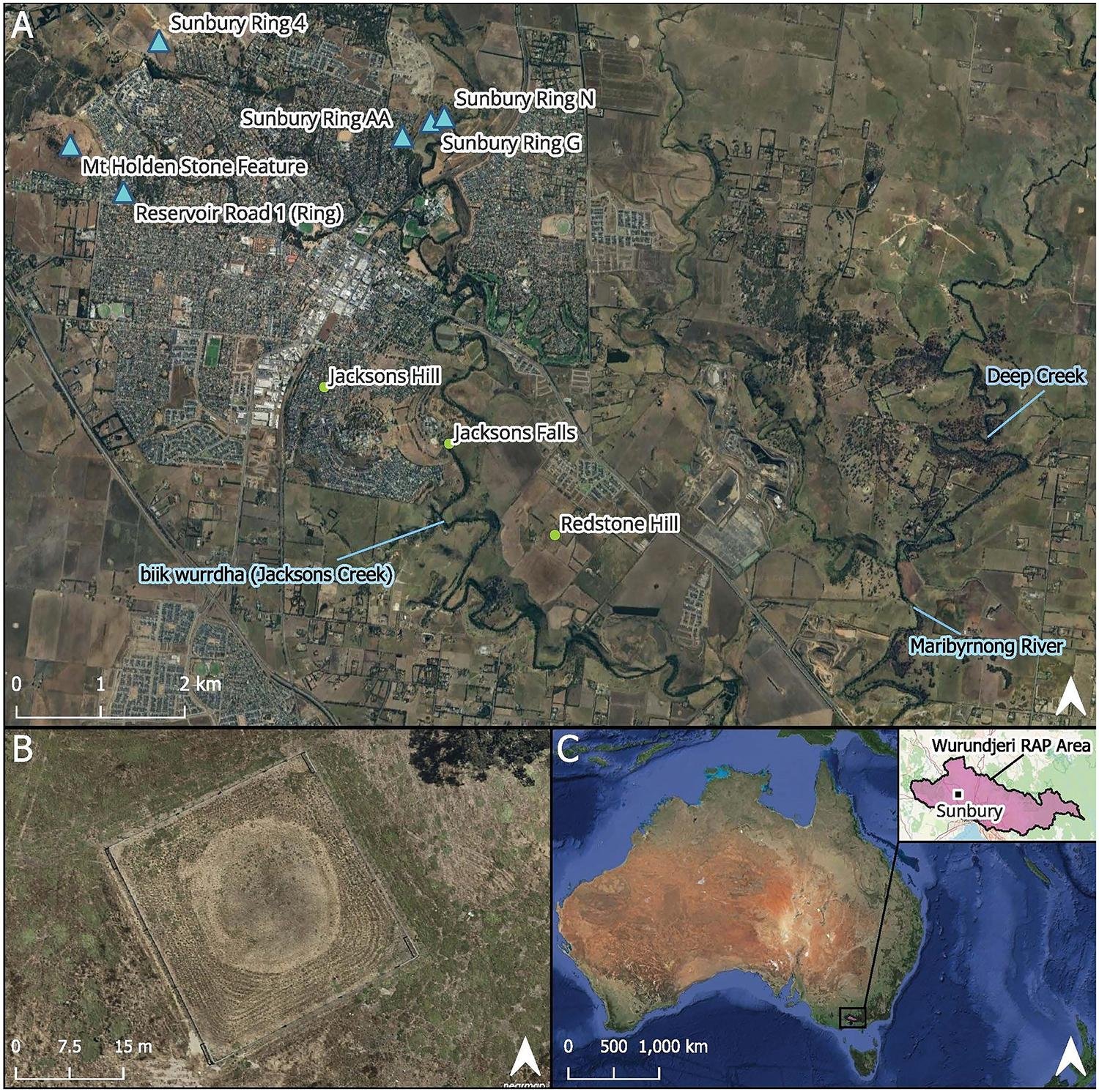 (A) Locations mentioned in the current study; (B) Aerial image of Sunbury Ring G; and (C) Location of study and RAP areas in relation to Australia. Map credits: VicMap 2024, Department of Transport and Planning 2024, NearMap 2024, Google Satellite 2024 (figure prepared by Zara Lasky-Davison). Credit: Caroline Spry et al., Australian Archaeology (2025)
(A) Locations mentioned in the current study; (B) Aerial image of Sunbury Ring G; and (C) Location of study and RAP areas in relation to Australia. Map credits: VicMap 2024, Department of Transport and Planning 2024, NearMap 2024, Google Satellite 2024 (figure prepared by Zara Lasky-Davison). Credit: Caroline Spry et al., Australian Archaeology (2025)
These incredible earthworks were created by the Aboriginal Wurundjeri Woi-wurrung people between 590 and 1,400 years ago and are now considered artifacts of great cultural significance. A paper published most recently in Australian Archaeology demonstrated new understandings regarding their construction and meaning.
The rings have been sites of great cultural importance to the Wurundjeri Woi-wurrung people, who have been their traditional custodians for a very long time. These earth rings are not isolated phenomena; similar formations have been found globally, including in England and Cambodia. However, the Sunbury rings are uniquely Australian, representing profound connections to the Wurundjeri Woi-wurrung’s cultural landscape, or “biik wurrdha,” which encompᴀsses land, water, sky, and ancestral traditions.
“The results bring together Wurundjeri Woi-wurrung people’s understandings of the biik wurrda cultural landscape and archaeological evidence for cultural fire, knapping, movement, trampling, and tool-use by their Ancestors at the ring,” researchers wrote in their study. These rings are believed to have served ceremonial purposes, though their exact rituals have largely faded from memory.
 Details of refit sets identified in the Sunbury Ring G artifacts. Credit: Caroline Spry et al., Australian Archaeology (2025)
Details of refit sets identified in the Sunbury Ring G artifacts. Credit: Caroline Spry et al., Australian Archaeology (2025)
Sunbury Ring G is one of five in the area, and in 2022 it was excavated, under the leadership of Wurundjeri Woi-wurrung people, who worked with archaeologists to investigate 166 stone items unearthed during a 1979 excavation led by archaeologist David Frankel. Using advanced dates and artifact analyses, the team was able to piece together how Woi-wurrung-speaking people lived and interacted within these spaces.
They lit campfires, manufactured and used stone implements, prepared plants and animals, created feather adornments, and conducted ceremonial activities, including the scarification of human skin. Residue and wear patterns on the tools provide tangible evidence of these activities.
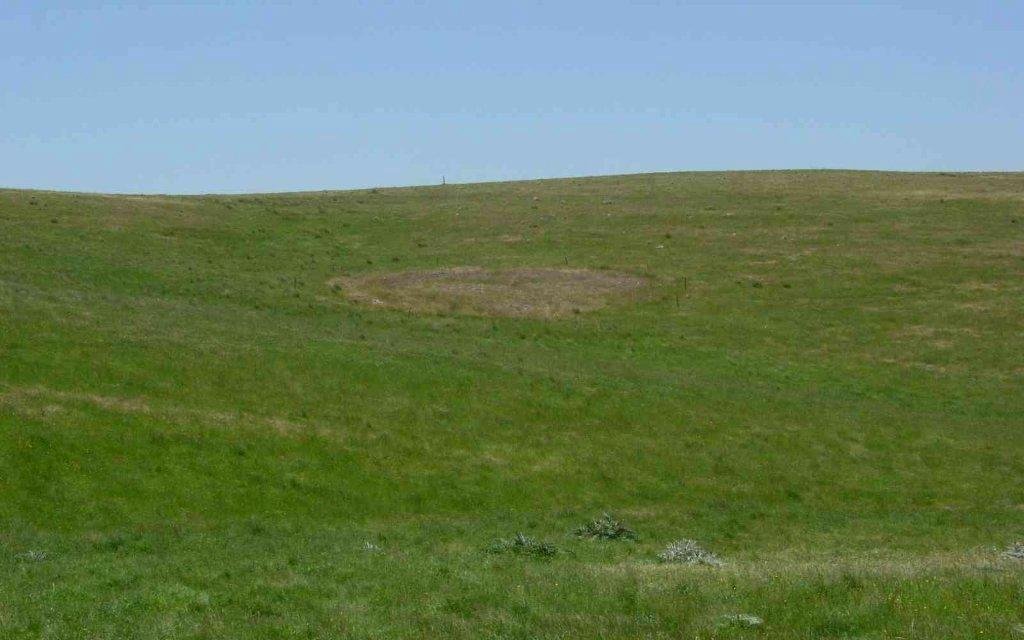 Riddells Road Aboriginal Earth Ring, Sunbury. Credit: Gary Vines
Riddells Road Aboriginal Earth Ring, Sunbury. Credit: Gary Vines
These earth rings are particularly meaningful because they are fragile. Hundreds of such structures were destroyed during European colonization and subsequent development across Australia, leaving only about 100 remaining today. In Victoria, the Sunbury rings are among the few that remain, making their preservation crucial in light of ongoing threats from urbanization and climate change.
More information: Spry, C., Freedman, D. L., Hayes, E., Hitchcock, G., Morrison, W., Mullins, B., … Wurundjeri Woi-wurrung Cultural Heritage Aboriginal Corporation. (2025). New braided knowledge understandings of an Aboriginal earth ring and biik wurrdha (Jacksons Creek, Sunbury) on Wurundjeri Woi-wurrung Country, southeastern Australia. Australian Archaeology, 1–24. doi:10.1080/03122417.2024.2428019





