Archaeological excavations in Hadrianopolis, in Turkey’s Karabük region, uncovered two game stones made of bone, dating to the 5th century CE. The stones provide a fascinating glimpse into the life of Roman soldiers and the playing of strategy board games in ancient times. This further elevates Hadrianopolis’s position as a Roman military garrison and a Roman cultural center.
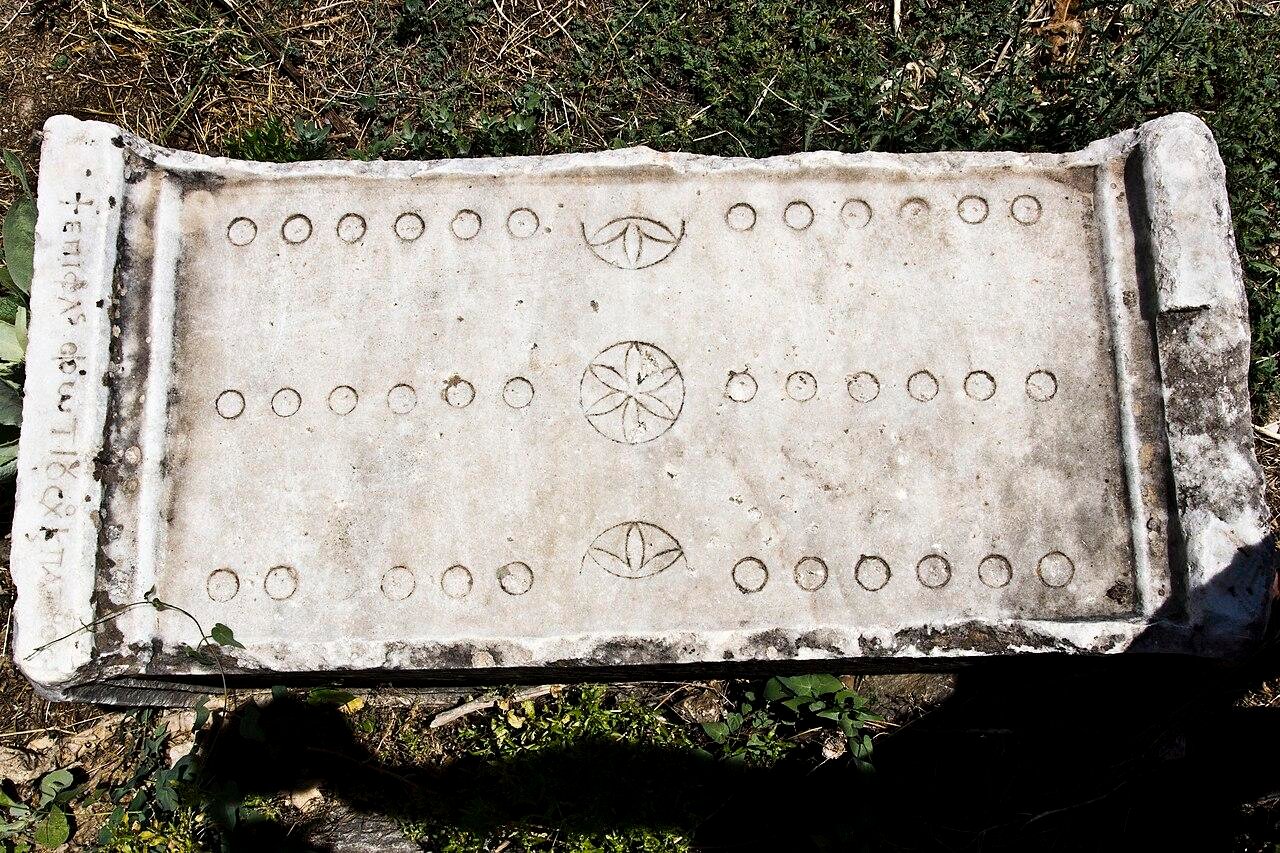 A Ludus Duodecim Scriptorum (“Twelve-lined Game”) from the second century CE, found at Aphrodisias. Credit: wneuheisel, CC BY 2.0
A Ludus Duodecim Scriptorum (“Twelve-lined Game”) from the second century CE, found at Aphrodisias. Credit: wneuheisel, CC BY 2.0
The bone game stones were unearthed in the 2024 excavation season by Karabük University Department of Archaeology ᴀssociate Professor Ersin Çelikbaş. Within the scope of the “Heritage for the Future” project by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, the excavation also aims to safeguard heritage and uncover new insights about the daily lives of ancient civilizations, their beliefs, and their structures.
The two stones, shaped like lentils and discs, have several symbols: one with a four-armed design, and the other with an eight-armed design with dots inscribed on them through scratching. These symbols weren’t decorative; they helped the gamers strategize. The stones were used in ancient Roman games like Ludus Latrunculorum (game of the robbers) and Duodecim Scripta (game of twelve lines), which were widely popular among the soldiers.
KBÜ Medya ile Karabük Üniversitesinin Başarıları Dünya Basınında Yer Almaya Devam Ediyor
Haber Linki: pic.twitter.com/lsC5hEXID1
— Karabük Üniversitesi (@krbkuni) January 20, 2025
The discovery of these game stones further confirms the existence of a Roman army in Hadrianopolis that likely included a cavalry garrison active between the 2nd and the 5th century CE.
Ludus Latrunculorum was a two-player strategy board game whose goal was to capture your opponent’s pieces through intelligence, foresight, and planning—skills that were required to be a warrior. Duodecim Scripta was played on a board with three rows of twelve squares.
Related: Researchers finally uncover how to play the 4,000-year-old Shahr-i Sokhta board game
Hadrianopolis, aptly described as the “Zeugma of the Black Sea” because of its stunning mosaics depicting various animals, including horses, elephants, and even mythological griffons, was an important part of the Roman Empire’s defense. It was situated near the eastern frontier of the empire and was therefore well-placed to defend against invasions from the Black Sea region.
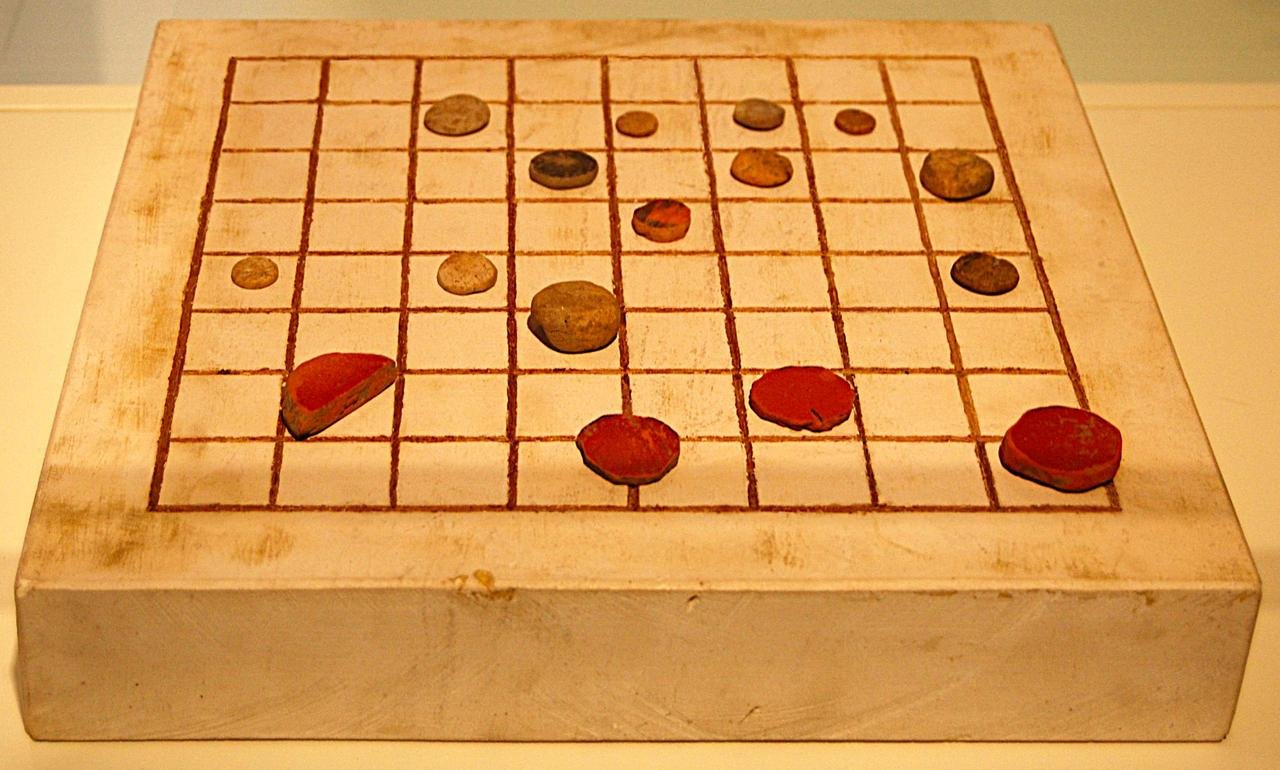 Ludus Latrunculi board, an ancient Roman strategy game, found in the Roman city of Complutum, Spain. Credit: Raimundo Pastor, CC BY-SA 4.0
Ludus Latrunculi board, an ancient Roman strategy game, found in the Roman city of Complutum, Spain. Credit: Raimundo Pastor, CC BY-SA 4.0
The city, founded as Orestias in ancient Greece, was renamed by Roman Emperor Hadrian in the 2nd century CE. It flourished particularly in the Chalcolithic, Roman, and Byzantine periods. Architectural remnants include Roman baths, a theater, villas, churches, rock-cut tombs, and monumental structures such as ceremonial niches.
Earlier excavations have also yielded evidence of the existence of a Roman army camp, such as a 3rd-century cavalry mask and barracks within the city. As excavations are scheduled to resume in 2025, researchers are hoping to unearth more artifacts.
More information: Karabük Üniversitesi





