A groundbreaking discovery in South Africa’s Kruger Cave has uncovered early humans’ sophisticated hunting techniques. Researchers have confirmed that one of the oldest documented multi-component poison coatings on weapons dates back 7,000 years. This new development brings to light information about early humans’ pharmacological knowledge and cognitive capabilities.
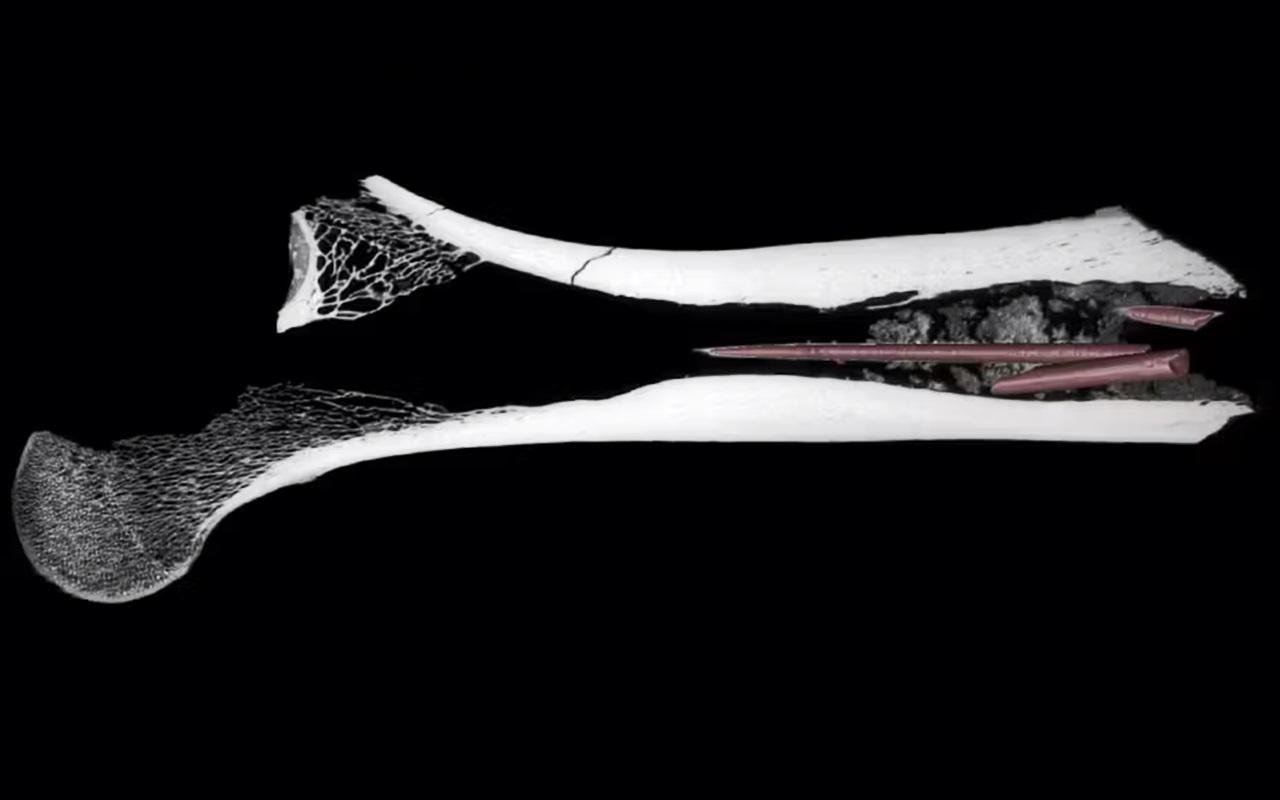 Micro-computed tomography (CT) segmented scan of the femur quiver clearly shows the three bone arrowheads embedded in the poison residue in the marrow cavity. Credit: Dr Aliénor Duhamel, CC BY-NC-ND
Micro-computed tomography (CT) segmented scan of the femur quiver clearly shows the three bone arrowheads embedded in the poison residue in the marrow cavity. Credit: Dr Aliénor Duhamel, CC BY-NC-ND
The artifact, an antelope femur bone, first appeared in 1983 and was stored at the University of the Witwatersrand’s Archaeology Department. It remained relatively unexamined for many years, but new digs at Kruger Cave in 2022 initiated new investigations focused on it. The femur bone contained three bone arrowheads inserted into its marrow cavity. Micro-CT scans, along with a variety of cutting-edge techniques, revealed that its cavity housed a sediment-like substance, with tests conducted afterward.
Chemical tests, published in iScience and led by Justin Bradfield at the University of Johannesburg, confirmed the presence of two cardiac glycosides, namely digitoxin and strophanthidin, which disrupt heart function. These chemicals, long ᴀssociated with bow hunting, were accompanied by ricinoleic acid, a byproduct of the potent toxin ricin. The presence of such chemicals in a mixture, deliberately blended from plant-based toxins, confirms early humans’ intentional use of poisons for efficient hunting.
“This is the oldest unequivocal complex hunting poison recipe yet identified, notwithstanding the many chemically unsupported ᴀssertions of older examples,” the researchers wrote in their study.
 Prehistoric hunting scene drawings in the Magura Cave, Bulgaria, between 10,000 and 8,000 years ago. Credit: Octopus, CC-BY-SA-3.0.
Prehistoric hunting scene drawings in the Magura Cave, Bulgaria, between 10,000 and 8,000 years ago. Credit: Octopus, CC-BY-SA-3.0.
Interestingly, the plants with such toxic compounds were not native to the surrounding environment of Kruger Cave. This suggests early humans traveled long distances to obtain these ingredients or participated in well-established networks of exchange. Long-distance transportation of shells and other goods has been observed through preceding studies, but the confirmation of botanical trade at such an early date is unprecedented.
The practice of poison use in hunting is believed to have started 60,000 to 70,000 years ago, coinciding with the development of projectile technology. Earlier poison use has been documented, such as in residues of ricinoleic acid on a 24,000-year-old spatula in Border Cave, but the discovery at Kruger Cave marks the oldest confirmed use of a complex mix.
Archaeobotany and organic analysis played critical roles in the discovery and demonstrate the synergy of multidisciplinary work in uncovering insights into early lifeway processes.
More information: Bradfield, J., Dubery, I. A., & Steenkamp, P. A. (2024). A 7,000-year-old multi-component arrow poison from Kruger Cave, South Africa. iScience, 27(12), 111438. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2024.111438





